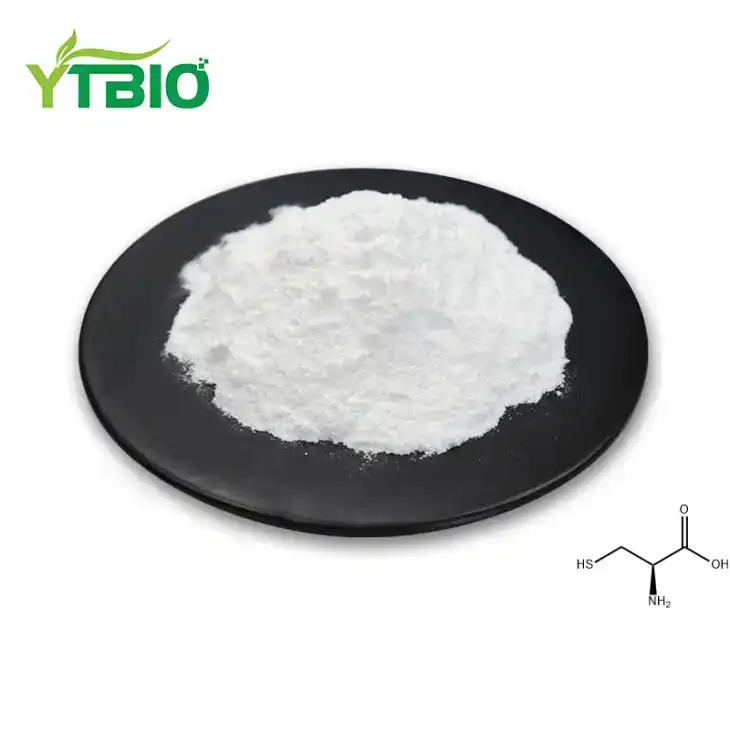
Cysteine Powder
Specification: 99%
Appearance: White powder
Packaging: 25kg/drum
Storage: Cool, Dry, Away From Light
Payment: T/T,VISA,XTransfer,Alipay......
Shipping Speed: 3-5 days
Certification:cGMP,ISO22000,ISO9001,EU&NOP Organic Certificate,Kosher,BRC,Halal,HACCP
- Fast Delievery
- Quality Assurance
- 24/7 Customer Service
Product Introduction
Cysteine Powder: Introduction
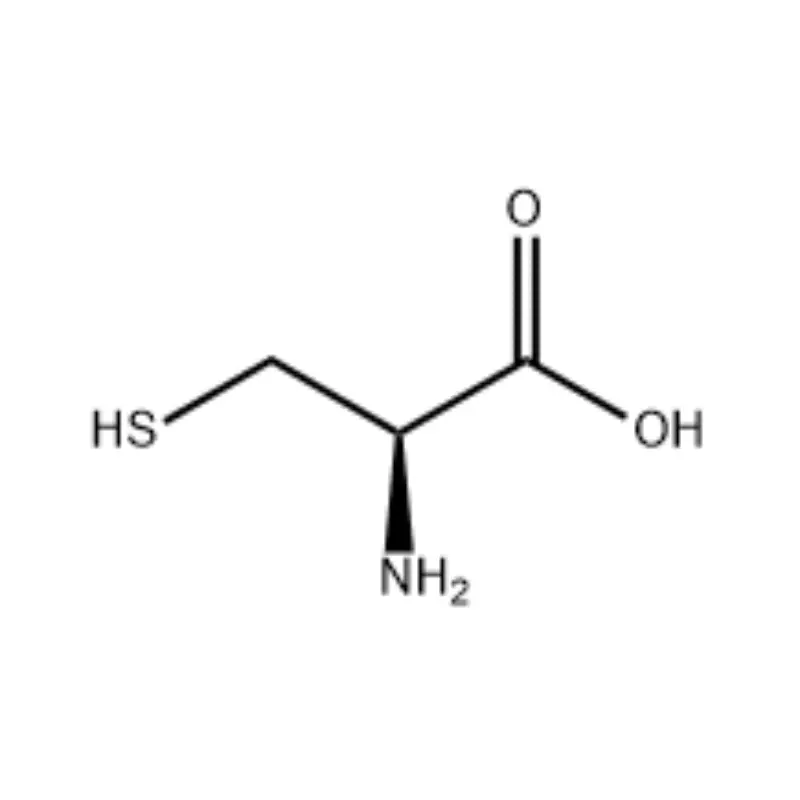
Cysteine powder is a sulfur-containing non-essential amino acid with the molecular formula C₃H₇NO₂S, which can be synthesized from other amino acids in the human body. As an important component of proteins, it is widely present in various proteins and glutathione, which has antioxidant effects. It plays a crucial role in maintaining skin elasticity, promoting collagen production, and regulating enzyme activity in the body. The sulfhydryl group (-SH) in its molecule is chemically active and easily oxidized. Two molecules of cysteine can be linked by a disulfide bond to form cystine, and the two can be interconverted in the body. This characteristic allows it to perform various physiological functions in the body, such as detoxification and antioxidation. It is widely used in food, medicine, cosmetics, and biochemical research. In the food industry, it is often used as a dough improver and antioxidant in bread processing and fruit juice preservation; in the medical field, it can be used for detoxification and protection against radiation damage; in cosmetics, it is used in perming and sunscreen products. In addition, it is also one of the key raw materials for the production of meat flavorings.
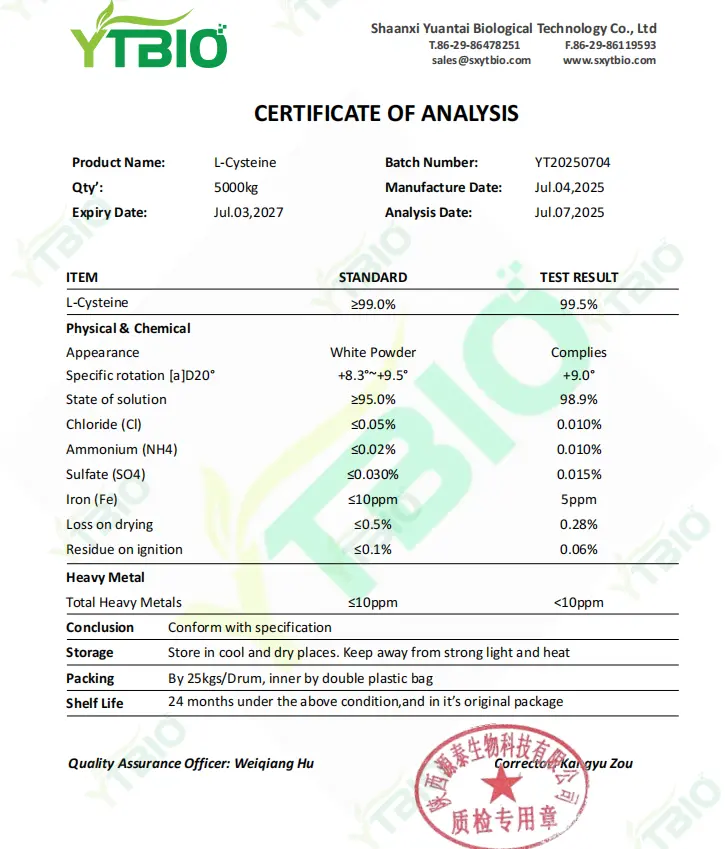
The Test Report For Cysteine Powder:
Cysteine Powder: Multiple Functions
Cysteine powder, as an indispensable sulfur-containing amino acid in the human body, has broad and profound physiological effects. It is not only a precursor for the synthesis of glutathione (GSH), a core antioxidant substance that effectively neutralizes free radicals and delays cell aging, but also a key molecule for maintaining internal homeostasis.
In terms of detoxification, cysteine can bind to various endogenous and environmental toxins (such as heavy metals, organic solvents, and peroxides) through its active sulfhydryl group (-SH), significantly enhancing the liver's detoxification capacity. This powerful integration not only provides protection against chemical liver damage but also participates in the elimination of metabolic waste such as alcohol and drugs.
For skin health, cysteine plays multiple roles: it inhibits excessive melanin production by regulating tyrosinase activity, thus helping to brighten skin tone and lighten dark spots; at the same time, as an important component of structural proteins such as keratin, it strengthens the skin barrier function, maintaining skin moisture and elasticity; in addition, it also has the potential to regulate keratin metabolism and assist in improving inflammatory skin problems. In the respiratory system, its derivatives (such as acetylcysteine), thanks to their unique thiol group, can break the disulfide bonds in mucus, effectively reducing sputum viscosity. Therefore, they are often used to improve respiratory symptoms in diseases such as chronic bronchitis and emphysema.
Cysteine also actively participates in tissue repair, promoting wound healing after surgery or burns. In terms of nutritional metabolism, it helps the body absorb and utilize iron and participates in the normal folding and structural stability of proteins.
However, its specific characteristics should also be noted: because it may affect insulin activity, diabetic patients should avoid self-supplementation; at the same time, it should be avoided by people with cystinuria to prevent exacerbating the risk of kidney stones. Overall, cysteine is an important cornerstone for maintaining the body's antioxidant defense, detoxification mechanisms, and skin and mucous membrane health.
Cysteine Powder: Main Food Sources
I. High-Quality Animal Sources
Animal foods are usually the most direct and abundant source of L-cysteine, due to their high protein content and amino acid composition similar to human needs.
Poultry and livestock meat: Lean cuts of chicken, turkey, pork, and beef are particularly rich in cysteine.
Eggs and dairy products: Eggs (especially egg yolks) and dairy products such as cheese and yogurt are also good sources.
II. Important Plant Sources
For vegetarians or those who wish to increase dietary diversity, various plant-based foods can also provide a certain amount of L-cysteine.
Legumes and products: Such as soybeans, tofu, and soy milk.
Whole grains and seeds: Oats, wheat germ, and nuts and seeds such as sunflower seeds and peanuts.
Some vegetables: Broccoli, onions, and garlic also contain this component.
Overall, a balanced intake of the above animal and plant-based foods is an effective way to ensure the body receives enough L-cysteine.
Cysteine Powder: Application Areas
Cysteine powder, as a key sulfur-containing amino acid, has found applications in several important industrial and health fields, including medicine, food, and cosmetics.
In the medical field, the core value of cysteine lies in its powerful antioxidant and detoxification capabilities. As a precursor to glutathione, it is crucial for protecting liver cells and assisting in the treatment of liver damage and drug poisoning. Its derivative, acetylcysteine, is a classic expectorant drug that effectively reduces sputum viscosity and is widely used in the management of chronic respiratory diseases. Furthermore, it has been studied for its potential in protecting against radiation damage and regulating immune function.
In the food industry, cysteine plays the role of a "multifunctional modifier." As a dough improver, it optimizes gluten structure, significantly improving the processing performance and softness of bread. It is also an effective antioxidant, used to protect nutrients (such as vitamin C) in foods like fruit juices and dairy products, preventing browning, maintaining flavor, and extending shelf life.
In the cosmetics and personal care industry, cysteine is favored for its beauty and skincare properties. It helps brighten skin tone and lighten blemishes by inhibiting melanin production, and its antioxidant properties contribute to anti-aging. In hair care products, it helps repair disulfide bonds in hair keratin, commonly found in perming agents and hair repair products to reduce damage and improve hair quality.
In addition, in the feed industry, cysteine is an important nutritional fortifier, used to supplement sulfur-containing amino acids in animal feed, especially for poultry and aquatic animals, to promote animal growth, improve feed utilization, and enhance immunity.
In short, from oral medications and nutritional supplements to everyday bread and fruit juices, and external skincare and hair care products, cysteine, with its unique chemical properties, serves many aspects of human health and life.

Cysteine Powder: Synthesis Methods
I. Biosynthesis Process
The synthesis pathway varies in different organisms:
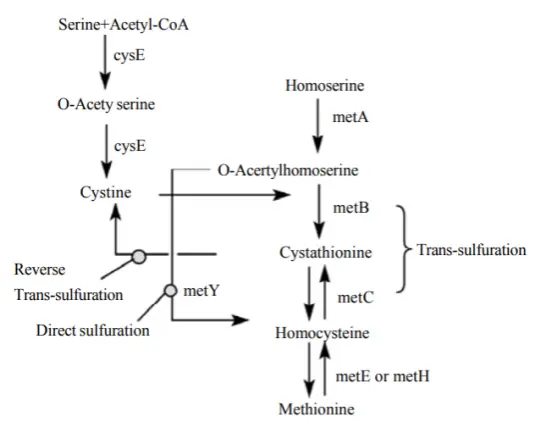
In animals: Cysteine powder is not synthesized directly from inorganic substances, but through a transsulfuration pathway, using methionine (which provides the sulfur atom) and serine as raw materials, converted via the intermediate product cystathionine.
In plants and microorganisms: They are able to convert inorganic sulfur into cysteine. The process involves first reducing sulfates in the environment to hydrogen sulfide, which then reacts with serine or its activated form (such as O-acetylserine) to ultimately synthesize cysteine.
II. Preparation and Synthesis Methods
In laboratory and industrial production, the following methods are mainly used to obtain L-cysteine or its hydrochloride:
Chemical Reduction Method (Tin Granule Reduction Method): This is one of the traditional methods. Cystine is dissolved in dilute hydrochloric acid, and tin granules are added for heating and reflux reduction. After the reaction, the solution is diluted, hydrogen sulfide gas is introduced to precipitate and remove excess tin ions, followed by filtration, concentration, and crystallization to obtain L-cysteine hydrochloride.
Electrolytic Reduction Method: A more modern preparation process. Cystine is dissolved in hydrochloric acid for electrolytic reduction. After electrolysis, the solution is also treated with hydrogen sulfide, followed by activated carbon decolorization, vacuum concentration, and cooling crystallization to obtain high-purity L-cysteine hydrochloride.
Protein Hydrolysis Method: Using natural proteins rich in cystine (such as human hair and pig bristles) as raw materials, concentrated hydrochloric acid is used for hydrolysis to obtain a mixture of hydrolysis products including cystine. The cystine is then separated and purified, and subsequently reduced to cysteine. This method was an important industrial source in the early days.
In summary, cysteine has specific metabolic pathways in living organisms, but in practical applications, it is mainly prepared from its oxidized form—cystine—through methods such as chemical reduction, electrolytic reduction, or post-treatment after protein hydrolysis.
YTBIO offers high-purity (≥99%) cysteine powder series products with stable and reliable quality, meeting the professional needs of various fields including food, cosmetics, and animal feed. Please contact us via email at sales@sxytorganic.com for detailed product information and professional solutions. We look forward to hearing from you and are committed to providing you with high-quality products and services.
_1737093401309.png)

