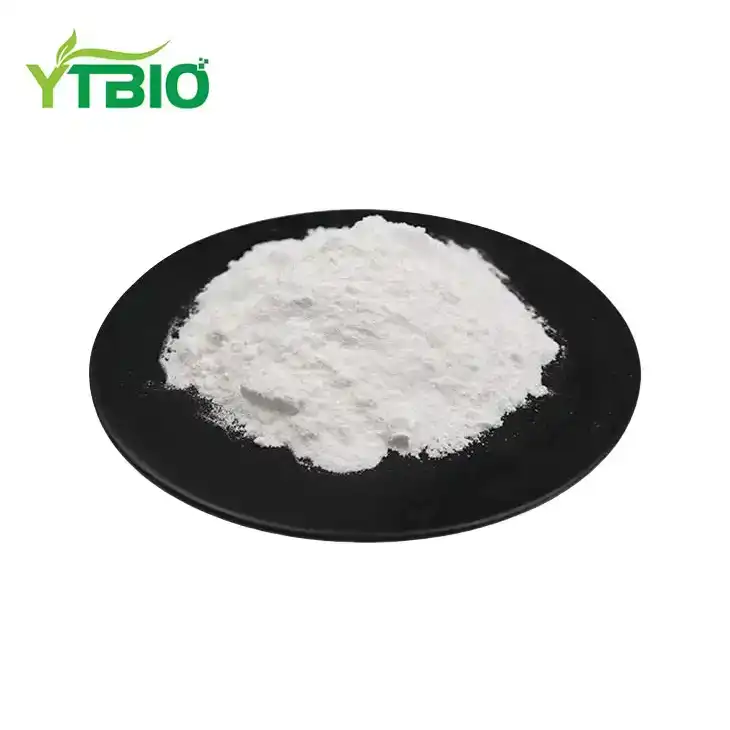
Magnesium Stearate Powder
Molecular Formula: C36H70MgO4
Molecular Weight: 591.24
EINECS: 209-150-3
Packaging: 25kg/drum
Storage: Cool, Dry, Away From Light
Payment: T/T,VISA,XTransfer,Alipay......
Shipping Speed: 3-5 days
Certification:cGMP,ISO22000,ISO9001,EU&NOP Organic Certificate,Kosher,BRC,Halal,HACCP
- Fast Delievery
- Quality Assurance
- 24/7 Customer Service
Product Introduction
Magnesium Stearate Powder: What is it?
Magnesium stearate powder, with the chemical formula C₃₆H₇₀MgO₄, is an organic salt formed from stearic acid and magnesium. It appears as a white, fine, and non-gritty powder with a characteristic slippery feel to the touch. Its core physical properties include insolubility in water, ethanol, and ether, but solubility in hot oils or hydrocarbon solvents. It decomposes upon contact with strong acids. As a versatile processing aid, its core value lies in its excellent lubricating and anti-adhesion properties, making it widely used in various industrial fields: in the pharmaceutical industry, it is a key lubricant in the production of tablets and capsules (typically added at 0.25%-5.0%), effectively preventing material adhesion and ensuring smooth production; in the food industry, it is used as an anti-caking agent and release agent in products such as milk powder and confectionery to improve flowability and appearance; and in cosmetics, it is used in powder products to enhance smoothness and adhesion. Overall, it is a widely used functional additive with low oral toxicity (LD50 >10g/kg).

Magnesium Stearate Powder: Functions and Applications
Magnesium stearate powder is a widely used functional excipient, whose core value lies in the multiple processing properties it provides, such as lubrication, anti-adhesion, and flow enhancement, due to its physicochemical properties.
Its mechanism of action can be summarized as follows: As a typical long-chain fatty acid salt, the polar magnesium ion end of its molecule firmly adsorbs to the surface of the material, while the non-polar long hydrocarbon chain is oriented outwards. This structure allows it to form an extremely thin molecular lubricating film with low shear force at the contact interface between particles or equipment, thereby significantly reducing friction and adhesion. Its microscopic lamellar crystal structure also facilitates uniform coverage.
Its main application areas are as follows:
Pharmaceutical preparations (the most important area): It is an indispensable core lubricant and flow enhancer in the production of tablets and capsules, ensuring smooth tableting, uniform filling, and preventing sticking to the punches. It should be noted that its hydrophobicity may delay drug dissolution, and the mixing process (time, intensity) significantly affects its effectiveness and tablet quality.
Food industry: As an anti-caking agent, emulsifier, and release agent, it is used to prevent caking in powdered foods such as milk powder and cocoa powder, and to improve the processing performance and texture of products such as chocolate and candy.
Cosmetics and personal care: Due to its smooth feel and adhesion, it is used in face powders, foundations, talcum powders, and some creams to improve product feel and spreadability.
Plastics, rubber, and other industrial fields: As a lubricant, release agent, and heat stabilizer (e.g., for PVC), it improves the processing flowability of materials and the surface finish of products.
Due to its extremely low oral toxicity, its use in pharmaceuticals and food is considered safe. However, its hydrophobicity and sensitivity to processing conditions (such as excessive mixing leading to decreased tablet hardness and slower dissolution) are critical points that must be precisely controlled in formulation and production.
Magnesium Stearate: Applications in Tablet Manufacturing
Lubricating Effect
During tablet compression, magnesium stearate powder effectively reduces friction between drug particles and between particles and the die. This makes the compression process smoother, helps improve production efficiency, and reduces the likelihood of tablet cracking and sticking to the die during molding. Its lubricating effect is particularly crucial in high-speed tablet presses to ensure consistent appearance and quality of tablets at high production volumes.
Anti-Adhesive Effect
For certain sticky drug components, magnesium stearate forms a protective film on the particle surface, effectively preventing adhesion between tablets or between tablets and the die after compression. This property improves the physical stability of the tablets, preventing clumping during subsequent packaging, storage, and transportation.
Flow-Promoting Effect
Magnesium stearate significantly improves the flowability of powders or granules. This allows the material to fill the die cavities of the tablet press more evenly and smoothly, ensuring that the weight variation of each tablet meets pharmacopoeial requirements and guaranteeing the uniformity of drug content. Good flowability is crucial for achieving automated, high-efficiency tablet production.
Precautions:
Improper Dosage May Affect Drug Release
If the amount of magnesium stearate is too high, it may lead to excessive lubrication and increased tablet hardness, thereby altering the drug release rate and pattern. It may also interact with specific drug components, interfering with the intended drug release characteristics. Therefore, its dosage must be precisely controlled through rigorous formulation screening and process optimization to ensure that drug release behavior meets the design objectives.
May Affect Tablet Disintegration
Magnesium stearate is hydrophobic, and the lubricating film it forms may hinder the rapid penetration of water into the tablet, thus delaying tablet disintegration. Delayed disintegration may further affect drug dissolution and in vivo absorption. During formulation development, its impact on disintegration should be evaluated, and compensation can be made by adjusting the type and amount of disintegrant or optimizing tablet hardness.
Potential Incompatibility with Certain Drugs
Magnesium stearate powder may have adverse chemical or physical interactions with certain drug active ingredients. For example, it may react with acidic drugs, affecting the chemical stability or bioavailability of the drug. Therefore, during the development phase of new drugs or formulations, it is essential to thoroughly study and verify their compatibility with the main drug and other excipients to avoid potential compatibility problems.
Is Magnesium Stearate Powder Safe?
Magnesium stearate powder is considered safe at typical usage levels, but its safety with long-term or high-dose intake still requires comprehensive consideration.
1. Safety Assessment and Acceptable Daily Intake
Magnesium stearate is classified as "generally recognized as safe" (GRAS) by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). According to reports cited by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), the upper limit for safe intake is approximately 2500 mg per kilogram of body weight. Based on this estimate, an adult weighing approximately 68 kg (150 lbs) could safely consume up to 170,000 mg of magnesium stearate daily. For reference, the typical amount of magnesium stearate added to a single capsule or tablet is only 4-8 mg, far below the safe limit.
2. Metabolism and Nutritional Value
Magnesium stearate breaks down into magnesium ions and stearic acid in the body:
Magnesium: An essential mineral for the human body, playing a vital role in maintaining heart function, muscle movement, nervous system stability, and energy metabolism.
Stearic acid: A common natural saturated fatty acid found in various foods such as beef tallow, cocoa butter, and vegetable oils. The body can convert it into energy or use it to build cell membranes. The daily intake of stearic acid from the diet (approximately 5700 mg/day for women and 8200 mg/day for men) is significantly higher than the amount of stearic acid contained in magnesium stearate from supplements.
3. Genotoxicity Study Results
To assess its potential genotoxicity, magnesium stearate has undergone several international standard tests, including:
Bacterial reverse mutation test (Ames test)
In vitro chromosomal aberration test
In vivo micronucleus test
All test results were negative, indicating that magnesium stearate did not show genotoxicity under the existing experimental conditions. This data has been used for safety assessments by organizations such as the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) and the Japanese government. 4. Usage Recommendations and Precautions
Although magnesium stearate is generally safe at conventional doses, the following should be noted:
Cumulative exposure risk: As a food additive, magnesium stearate is widely present in various products such as supplements, medications, candies, and baked goods. While the amount in a single product is low, the long-term health effects of cumulative intake of magnesium and other additives from multiple sources still require further research.
Individual differences: Individuals sensitive to magnesium stearate may experience digestive discomfort. It is recommended to use related products under the guidance of a doctor or nutritionist.

As a professional supplier of magnesium stearate , YTBIO consistently adheres to a quality system as its core principle, ensuring that every batch of product meets the application needs of global customers in terms of stability, safety, and compliance. We have obtained numerous international authoritative certifications, including cGMP, ISO22000, ISO9001, EU & NOP Organic, Kosher, BRC, Halal, and HACCP, enabling us to provide reliable and traceable raw material solutions for the dietary supplement, food, and pharmaceutical industries. YTBIO is committed to establishing long-term and stable supply relationships with our partners. For technical data, specifications, or business cooperation information regarding magnesium stearate, please feel free to contact sales@sxytorganic.com.
_1737093401309.png)

