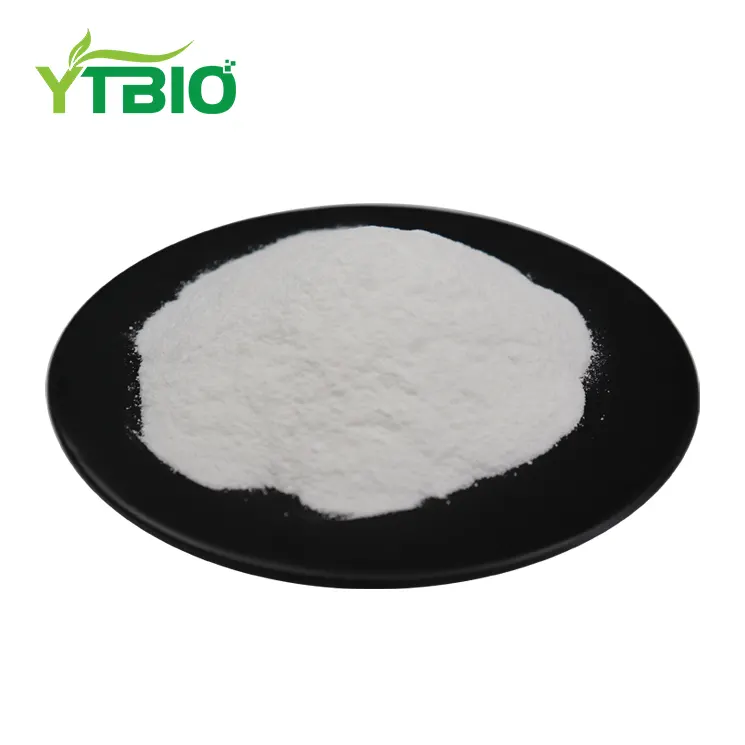
Birch Bark Extract Powder
Assay: 98%
Test:HPLC
CAS: 472-15-1
Molecular Formula: C30H48O3
Melting Point: 295-298°C
Appearance:White Crystalline Powder
Source of Supply: Factory Supply Directly
Storage conditions: This product should be sealed and shaded, stored in a dry
Certifications:cGMP,ISO22000,ISO9001,EU&NOP Organic Certificate,Kosher,BRC,Halal,HACCP
Shipping speed:3-5 days
- Fast Delievery
- Quality Assurance
- 24/7 Customer Service
Product Introduction
Do You Know About Birch Bark Extract Powder?
The main component of birch bark extract powder is betulinic acid.
Betulinic acid (BA) is a pentacyclic triterpenoid compound with a lupane-type structure. First discovered in plantain in 1902, it has since been found in plants such as birch bark and birch sap. Its molecular formula is C30H48O3, and its molecular weight is 456.71. It exhibits various pharmacological activities, including anti-inflammatory and antiviral activities.

Betulinic acid can be obtained from a variety of biological sources, including extracts from syzygium wilfordii leaves, birch bark, and jujube seeds. It can also be obtained through chemical synthesis of betulin.
YTBIO: Professional Birch Bark Extract Powder(Betulic Acid) Manufacturer and Supplier
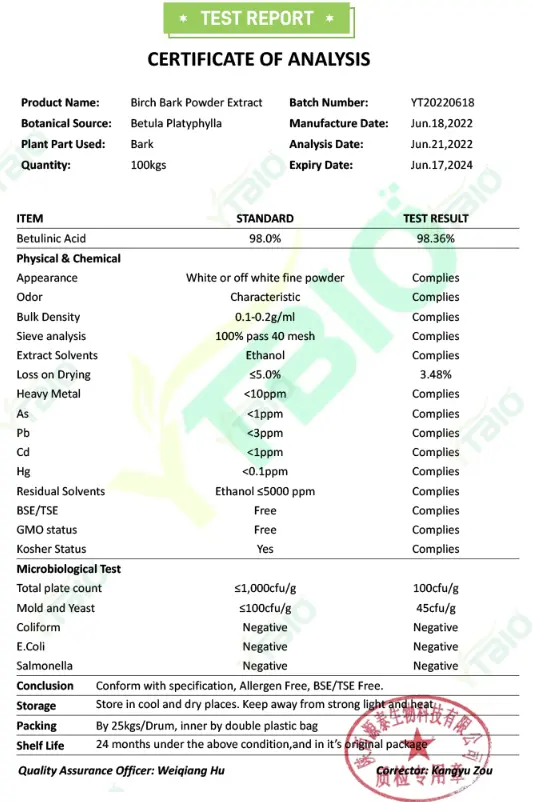
Main Effects of Birch Bark Extract Powder(Betulic Acid)
1. Anti-tumor Effects
Btulinic acid exhibits selective cytotoxicity against various tumor cells, including melanoma, glioblastoma, colon cancer, and breast cancer, inducing apoptosis and inhibiting tumor cell proliferation.
2. Anti-inflammatory Effects
Btulinic acid reduces inflammation by inhibiting protein kinase C (PKC) and prostaglandin synthesis, and has a certain effect on inflammatory-related diseases such as arthritis and liver fibrosis.
3. Antiviral Effects
Btulinic acid has inhibitory effects on HIV-1 and herpes simplex virus (HSV), and its mechanism may involve interfering with viral replication or regulating host cell function.
4. Other Effects
Antioxidant Effects: It scavenges free radicals and reduces oxidative stress.
Immunomodulatory Effects: It affects immune cell function and regulates immune responses.
Metabolism Modulation: Studies have shown that it may have potential therapeutic effects on metabolic syndromes such as diabetes and hyperlipidemia.
Source and Production of Birch Bark Extract Powder(Betulic Acid)
Traditionally, betulinic acid is extracted from birch bark, but the content is extremely low (approximately 0.025%), making extraction costly. In recent years, microbial fermentation (such as heterologous synthesis using Saccharomyces cerevisiae) has become a more efficient production method, significantly increasing yields.
Bitulinic acid and its derivatives are used not only in medical research but also in skincare products, primarily for moisturizing and skin barrier repair.
Betulinic Acid And Its Derivatives Can Protect Common Diseases
Protecting cardiomyocytes
Btulinic acid and its derivatives can protect cardiomyocytes by regulating cell signaling pathways. For example, betulinic acid can alleviate myocardial hypoxia/reoxygenation injury by inducing Nrf2/HO-1 and inhibiting p38 and JNK pathways. It can also inhibit TGF-β1/Smad signaling, thereby preventing high-glucose-induced expression of extracellular matrix proteins in cardiac fibroblasts and treating cardiac fibrosis, thereby protecting cardiac cells. Betulin can inhibit PI3K/AKT activity, thereby reducing AGE-induced autophagy in H9C2 cardiac cells. The betulinic acid derivative BA5-2 can alleviate inflammation and fibrosis in experimental chronic Chagas cardiomyopathy by inducing interleukin-10 and M2 macrophage polarization.
Liver-protective effects
Btulinic acid and its derivatives can also play a role in lipid regulation and liver protection. Betulinic acid and its derivatives can prevent ethanol-induced fatty liver disease; mice fed a high-fat diet with betulinic acid significantly suppress obesity; betulinic acid also inhibits non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and reduces total cholesterol and triglyceride levels. Two possible mechanisms of betulinic acid's anti-obesity effects are AMPK activation and reduced intestinal cholesterol absorption. Modulating the AMPK-SREBP signaling pathway helps reduce hepatic lipid accumulation; and reducing intestinal cholesterol absorption by inhibiting human cholesterol acyltransferase-1 (responsible for foam cell formation in macrophages) and human cholesterol acyltransferase-2 (responsible for cholesterol absorption in intestinal mucosal cells).
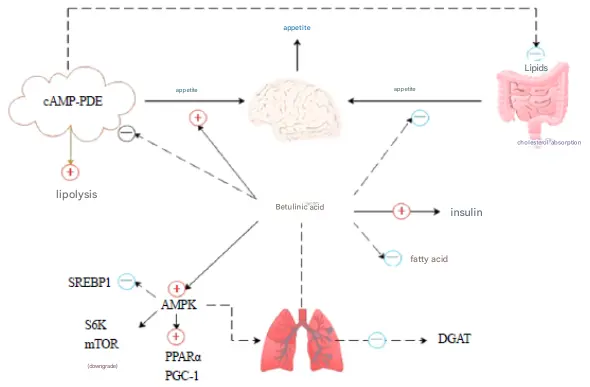
Effects of betulinic acid on glucose metabolism
Antibacterial Effects
Bucholic acid and its derivatives exert their antibacterial effects by inhibiting bacterial and fungal biofilms. Betulinic acid and betulinol can inhibit the growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa colonies and reduce their biofilm formation. Betulinol, betulinic acid, and ursolic acid enhance electron transport chain activity in Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Staphylococcus aureus, inducing and increasing ROS production, leading to lipid peroxidation and DNA fragmentation, and ultimately bacterial death. Betulinic acid can also inhibit Staphylococcus aureus by inhibiting peptidoglycan formation. Betulinic acid-amide compounds also exhibit inhibitory effects against Streptococcus mutans and Bacillus cereus.
Inhibit diabetes and its complications
Diabetes is one of the major diseases that humans currently face. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors γ (PPARγ) play an important role in regulating glucose metabolism and lipid balance. Betulinic acid, as a PPARγ antagonist, can inhibit diabetes by promoting osteoblast differentiation and inhibiting adipogenesis. Betulinic acid has two main mechanisms of action in inhibiting diabetes:
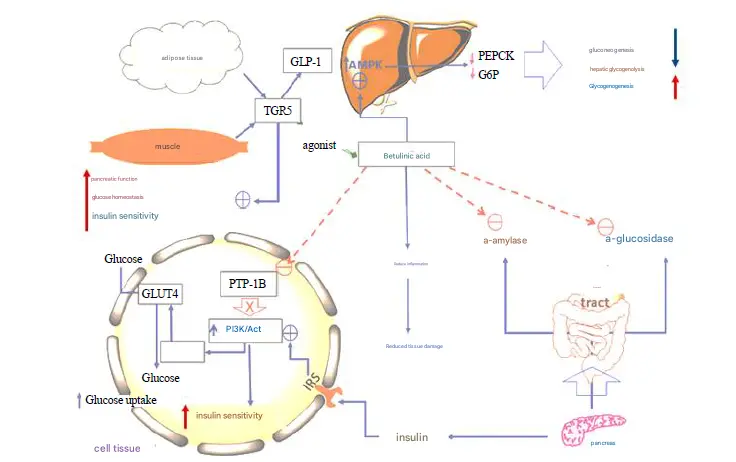
Regulation of lipid homeostasis, metabolism and oxidation by betulinic acid
(1) Inhibiting α-amylase and α-glucosidase, reducing the hydrolysis of polysaccharides, reducing the content of free glucose, and thus reducing the body's absorption of sugars;
(2) By activating AMPK, it reduces the expression of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and glucose-6-phosphatase, while increasing glucose transport across the cell membrane and promoting the expression of glucose transporters GLUT-1 and GLUT-2 to promote glucose uptake and glycogen synthesis.
Betulinic acid substances can also inhibit the occurrence of diabetic complications. For example, betulinic acid can improve proteinuria in experimental membranous nephropathy by regulating the Nrf2/NF-κB pathway.
Birch Bark Extract Powder:Betulinic acid and Betulinol
Betulinic acid and betulin are two closely related natural pentacyclic triterpenoids, widely found in the bark of birch (Betula alba). They share similar structures and are often collectively referred to as "birch triterpenes."However, their structural differences—one is acidic, the other an alcohol—lead to significant differences in their biological activities, pharmacological mechanisms, and applications.

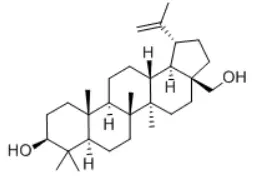
Betulinic acid and Betulinol
Source and Structure
Same Source: Both are widely found in birch bark, Betula spp., and some Eucalyptus plants.
Transformation Relationship:
Butulin can be converted to betulinic acid through enzymatic oxidation or chemical reactions, making the former often used as a raw material and precursor for the latter.
Comparison Note
Butulinic acid has a carboxylic acid group (–COOH) at the C-28 position.
Butulinol has a hydroxyl group (–CH2OH) at the same position.
This small change results in differences in their lipophilicity, membrane permeability, and receptor binding sites.
Chemical properties
Betulinic Acid:
It is a pentacyclic triterpenoid with a lupane-type backbone.
Its terminal carboxyl group (–COOH) makes it highly reactive.
It can undergo a variety of derivatization reactions, including esterification, amidation, and carboxylic acid reduction.
It serves as the starting nucleus for many drug design reactions.
Betulin:
It also has a lupane backbone, but contains two hydroxyl groups (C-3 and C-28).
The hydroxyl groups provide good modification sites.
It is easily converted to betulinic acid or betulonic acid through oxidation.
It is one of the most abundant pentacyclic triterpenes in natural products.
Differences in efficacy and application
|
|
|
|
|
|
Exhibits selective toxicity, with minimal effect on normal cells |
|
|
|
Commonly used in high-end anti-aging formulas |
|
|
|
|
|
While the chemical structures of betulinic acid and betulinol are similar, they each possess distinct strengths in their efficacy and applications. Understanding their mechanisms and differences is crucial for optimal pairing and precise development.
YTBIO is committed to providing customers with the highest quality Birch Bark Extract Powder (98% Betulinic Acid) and services. If you have any questions or needs about our products, please feel free to contact us and we will respond to you as soon as possible.
_1737093401309.png)

