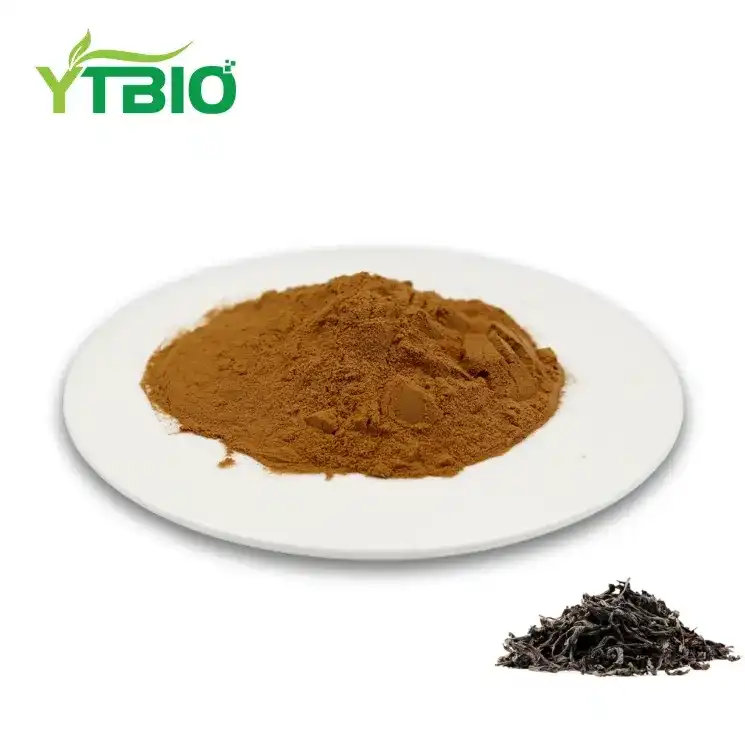
Bulk Oolong Tea Extract
Appearance:Brown Powder
Main ingredients:Polyphenols,Polysaccharides,Proteins, amino acids, vitamins, etc.
Application:Medical,Cosmetic,Food field
Package: 25Kg/barrel
Shipping speed: 3-5 days
Storage Conditions: Cool And Dry Place
Payment: T/T,VISA,XTransfer,Alipay
Certificates: cGMP,ISO22000,ISO9001,EU&NOP Organic Certificate,Kosher,BRC,Halal,HACCP
- Fast Delievery
- Quality Assurance
- 24/7 Customer Service
Product Introduction
Introduction to Bulk Oolong Tea Extract
Oolong tea is a semi-fermented tea, a unique tea variety in China. Oolong tea has a natural floral and fruity aroma, and has both the fragrance of green tea and the mellow taste of black tea, which makes oolong tea different from other teas. The overall taste of tea is rich and mellow, and contains a variety of active organisms such as tea polyphenols, alkaloids and theanine, which can effectively resist oxidation.
Bulk Oolong tea extract is a natural compound extracted from oolong tea. It is rich in a variety of bioactive ingredients and has multiple health benefits. It is widely used in food, cosmetics and medicine. The following is a brief introduction to oolong tea extract.
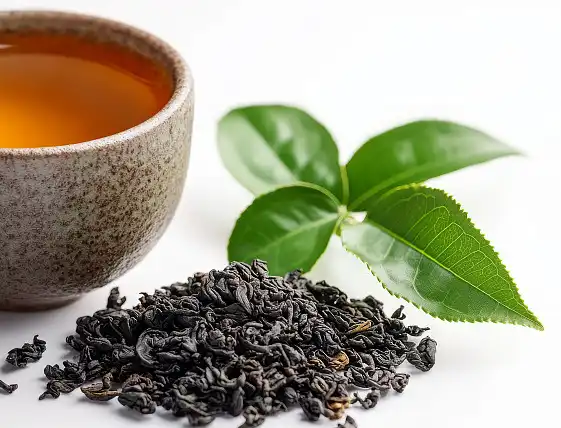

Main ingredients of Bulk Oolong Tea Extract in Skin Care
Tea polyphenols: The main active ingredient, with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
Caffeine: It has the effect of refreshing the mind and promoting fat decomposition.
Tea polysaccharides: It helps regulate blood sugar and enhance immunity.
Theanine: It has the effect of relaxing nerves and improving memory.
......
Main effects of Bulk Oolong Tea Extract in Skin Care
Antioxidant: It effectively removes free radicals and delays the aging process.
Weight loss: It promotes fat metabolism, reduces blood lipids and cholesterol.
Improve cardiovascular health: It reduces blood viscosity and prevents cardiovascular diseases.
Beauty and skin care: It inhibits tyrosinase activity, reduces melanin synthesis, and has a whitening effect.
Application areas of Bulk Oolong Tea Extract in Skin Care
Medical field: It is used to develop drugs for antioxidant, weight loss and maintenance of cardiovascular health.
Cosmetic field: Used in skin care products, with whitening, anti-aging and other effects.
Food field: Used as a natural additive in beverages, health foods, etc. to enhance the health value of products.
What are the types of tea extracts and their skin care effects?
What kind of tea does "tea extract" refer to?
Can black tea, green tea and white tea all come from the same tea tree? The answer is of course they can.According to China's national standard for "tea classification", tea products are divided into seven categories based on the degree of fermentation caused by the processing technology: green tea (fermentation degree 0~5%), white tea (5~10%), yellow tea (10~20%), oolong tea (15~70%), black tea (70~90%), dark tea (100%) and reprocessed tea. In theory, the same tea tree can be made into any variety of tea using different processes. But in reality, what kind of tea to make is still determined by the adaptability of the tea itself and market factors. Therefore, white tea, green tea and black tea can all be written as tea extracts in the product.

What is the use of tea extracts in cosmetics?
The composition of tea is very complex. At present, more than 1,400 substances have been found in tea, such as tea polyphenols, purines, amino acids, proteins, vitamins, mineral elements, tea saponins, etc. Some ingredients have skin care effects, such as:
·Tea polyphenols
Tea polyphenols are the most widely used concept in cosmetics, and they have also been widely recognized by consumers.
Tea polyphenols have extremely strong antioxidant effects, which can alleviate various skin damage caused by free radicals, and have skin care effects of anti-radiation, sun protection, and prevention of spots. Due to different preparation processes, green tea is the tea with the most tea polyphenols, followed by white tea, and black tea is relatively low. If you want tea polyphenols, green tea is definitely the first choice.
·Tea saponins
Tea saponins extracted from tea seeds are a mild non-ionic surfactant with good foaming and stabilizing abilities, and are not affected by water hardness, and can be used in washing and care products.
·Theanine
Theanine is a relatively rare amino acid in general plants and a relatively unique ingredient. However, cosmetics containing the ingredient "theanine" in their names only began to appear in 2017, and there is hope for the future.
·Tea pigments
During the fermentation process, black tea and dark tea form special ingredients and functions due to the participation of microorganisms. Tea pigments are one of the important ingredients, and tea pigments are divided into theaflavins, theabrownins, and thearubigins. Unlike the antioxidant activity of tea polyphenols, theaflavins have a stronger effect in inhibiting the activity of lipoxygenase, so theaflavins have a better function of lowering blood lipids, so it is often said that drinking black tea to lose weight is also theoretically based.
·Flavones
During the storage of white tea, theanine reacts with catechins to form white tea flavanones (EPSF), which is an important component of white tea to exert its health function. Its content continues to increase with the extension of storage years. White tea flavanones have certain anti-inflammatory and damage repair effects, and also have strong antioxidant activity. They are often used as ingredients in soothing lotions.
In addition, polysaccharides, alkaloids, aromatic substances, vitamin groups, etc. in tea are also important ingredients to be explored in the concept of tea.
The anti-inflammatory secret of tea extract: the magical effect of tea polyphenols
When you drink tea, the polyphenols in tea (especially epigallocatechin gallate, EGCG) play a significant anti-inflammatory role in the body. As the most biologically active monomer component of tea polyphenols, it accounts for about 50% to 70% of the total amount of tea polyphenols. EGCG intervenes in the inflammatory response pathway through a multi-target regulatory mechanism.
Anti-inflammatory mechanism at the molecular level
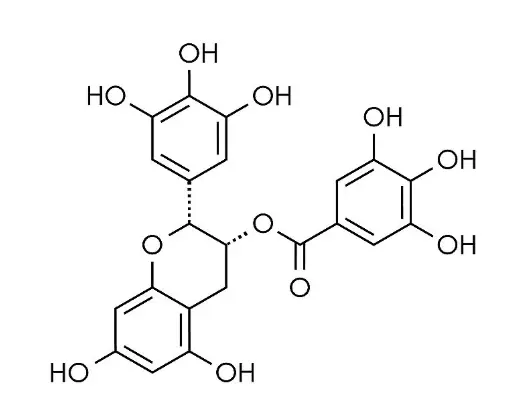
EGCG (Epigallocatechin gallate)
The core regulatory factor of the inflammatory response is nuclear transcription factor-κB (NF-κB), which binds to the inhibitory protein IκB to form a complex in the cytoplasm in the resting state. When the body is stimulated by pathogen infection, tissue damage or oxidative stress, IκB kinase (IKK) is activated, resulting in phosphorylation and degradation of IκB, thereby releasing NF-κB. Free NF-κB then translocates to the cell nucleus, binds to specific DNA sequences, and upregulates the transcriptional expression of pro-inflammatory mediators such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2).
Studies have shown that epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) can inhibit the activation of NF-κB by blocking IKK phosphorylation, inhibiting NF-κB nuclear translocation, and downregulating inflammatory gene expression.This mechanism suggests that EGCG exerts multi-level anti-inflammatory effects by targeting key nodes in the NF-κB signaling pathway, providing a potential molecular target for the intervention of inflammatory-related diseases.
Scavenging free radicals and activating the antioxidant enzyme system in the body
Inflammation is closely related to oxidative stress and exacerbates each other. Inflammation produces a large number of free radicals, which in turn exacerbate inflammation. There are multiple phenolic hydroxyl groups in the molecular structure of tea polyphenols, which can quickly capture free radicals and play a direct antioxidant role, with an efficiency more than 3 times that of vitamin C. They can also activate the body's antioxidant enzyme system (such as superoxide dismutase), play an indirect antioxidant role, and form a double protection network.
For example, when ultraviolet rays cause skin inflammation, topical application of tea polyphenols can significantly reduce redness and swelling.
Regulate the stability of intestinal flora
Recent studies have revealed that tea polyphenols can promote the proliferation of probiotics such as bifidobacteria in the intestine, while inhibiting pathogenic bacteria such as Salmonella. These probiotics produce short-chain fatty acids (such as butyric acid), which can not only repair the intestinal mucosal barrier, but also regulate the level of systemic inflammation through channels such as the "gut-brain axis". Studies have shown that the proportion of anti-inflammatory bacteria in the intestinal flora of regular tea drinkers is 15%-20% higher than that of non-tea drinkers.
Indirect anti-inflammatory effect of tea polyphenols
In addition to the direct anti-inflammatory effect of the first three steps, tea polyphenols can also indirectly reduce the level of systemic inflammation, taking the anti-inflammatory ability to a higher level. For example, the accumulation of excessive sugars and lipids can lead to increased levels of inflammation in the body. Tea polyphenols can indirectly play an anti-inflammatory role by changing the catalytic activity of digestive enzymes in the intestine and maintaining the balance of sugar and lipid metabolism in the body. For example, EGCG has a good inhibitory effect on a variety of digestive enzymes (such as maltase, sucrase, isomaltose and α-glucosidase). On the other hand, tea polyphenols can reduce the absorption of sugars by inhibiting the intestinal epithelial glucose transporter, and also reduce the absorption of fat by inhibiting the synthesis and secretion of apolipoprotein B48.
How to achieve anti-inflammatory effects through drinking tea scientifically?
If you want tea polyphenols to play a better anti-inflammatory role, you can refer to the following points:
1. Brewing water temperature
Studies have shown that different substances contained in tea require different water temperatures for soaking. Tea polyphenols and caffeine are quickly leached at high water temperatures, and the tea soup is bitter; at low water temperatures, they are slowly leached, and the tea soup is less bitter.
2. Develop a habit of drinking tea regularly
Tea polyphenols are metabolized quickly in the body, and drinking a large amount at one time is not as good as drinking it in divided and regular times. For most healthy adults, drinking the equivalent of 3-4 cups (about 600-1000 ml) of tea a day is a more appropriate reference amount. You can also drink it at different times of the day according to your personal habits.
3. Use scientific combinations
Vitamin C can help increase the absorption rate of EGCG in the body. Therefore, while drinking tea or after drinking it, eating some fruits rich in vitamin C (such as citrus, strawberries, kiwis, etc.) may have a 1+1>2 effect.

Combination of EGCG and Vitamin C
4. Pay attention to your personal constitution and gastrointestinal protection
Tea polyphenols and caffeine are irritating to the gastrointestinal tract of some people. If you have a sensitive stomach or have experienced discomfort when drinking tea on an empty stomach, it is recommended to drink tea half an hour after a meal. Everyone has a different constitution, and it is most important to find the rhythm and timing of tea drinking that suits you.
It should be noted that although laboratory data show that tea polyphenols have significant anti-inflammatory effects, more research is still needed to verify its clinical efficacy. However, drinking tea as part of a healthy lifestyle also has many benefits for personal health and long-term fight against inflammation.
As a professional manufacturer of oolong tea extract, YTBIO has own factory, quality inspection and R&D team. We are committed to providing customers with the best quality Bulk oolong tea extract powder and services. It is our original intention to allow every consumer to enjoy high-quality and healthy products. If you have any needs or questions about our products, please feel free to contact us at sales@sxytorganic.com and we will reply you as soon as possible.
_1737093401309.png)

