LBG Locust Bean Gum
Appearance: White to Light Yellow Powder
Source: Fructus Sophorae
Specifications: 800,1500-2000,3000,6000 viscosity
Application: Food and health products
Shipping speed:1-3 days
Inventory:In stock
Package:25Kg/barrel
Certificates:cGMP,ISO22000,ISO9001,Kosher,BRC,Halal,HACCP
- Fast Delievery
- Quality Assurance
- 24/7 Customer Service
Product Introduction
Do You Know Locust Bean Gum?
LBG Locust Bean Gum, abbreviated as lbg, is also known in chinese as carob bean gum and locust bean gum. locust bean gum is a polysaccharide compound composed of galactose and mannose residues. the finished product is a white to yellow powder granules. the transparency of locust bean gum varies significantly depending on the extraction process, particle size, and purity. it also has synergistic effects with other gums.
Locust bean gum is derived from a drought-resistant locust tree that grows along the Mediterranean coast. The tree grows slowly, producing beans in large quantities after about 15 years and reaching maximum yield after 50 years.

LBG Locust bean gum is widely used in the food industry and can be used in many foods, including jellies, jams, ice cream, and popsicles.As a food additive, it is widely used for thickening, stabilization and emulsification. It also has certain health benefits, such as regulating intestinal function and assisting in controlling blood sugar.
Characteristics of LBG Locust Bean Gum
Locust bean gum appears as a white to yellow powder, granules, or flat flakes, and is odorless and tasteless. It disperses in cold water, partially dissolving to form a sol and completely dissolving at 80°C. Its pH range is 5.4-7.0, and the addition of a small amount of sodium borate converts it into a gel. Within the pH range of 3.5-9.0, viscosity is largely unaffected by pH. Viscosity decreases with a pH below 3.5 or above 9.0. Inorganic salts such as NaCl, MgCl₂, and CaCl₂ have no effect on viscosity, but acids (especially inorganic acids) and oxidants can cause salting out and degradation, reducing viscosity. Adding gelatin, carrageenan, or sucrose, glucose, or glycerol to the aqueous solution can prevent salting out to a certain extent. Locust bean gum interacts with agar, carrageenan, and xanthan gum, forming complexes in solution that enhance the gelling effect.
YTBIO: LBG Locust Bean Gum Manufacturer And Supplier

Health Benefits of LBG Locust Bean Gum
1. Intestinal Health
Locust bean gum is a water-soluble fiber that promotes intestinal motility and relieves constipation. It also acts as a prebiotic, promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria and improving the intestinal microbiome.
2. Assists in Blood Sugar Regulation
Research shows that its gel properties can delay gastric emptying and slow glucose absorption, potentially benefiting postprandial blood sugar management in diabetic patients.
3. Assists in Cholesterol Regulation
Some studies have shown that locust bean gum can bind to bile acids, promote cholesterol metabolism, and lower low-density lipoprotein (LDL) levels in the blood.
4. Low in Calories
As a colloid, locust bean gum is barely absorbed by the body, making it suitable for those who need to control their calorie intake (e.g., as a meal replacement or low-calorie food).
Main Functions Of LBG Locust Bean Gum In The Food Industry
Main Functions
1. Thickening and Stabilizing
LBG Locust bean gum forms a highly viscous solution when dissolved in water. It is often combined with xanthan gum, carrageenan, and other ingredients to enhance food texture. For example, it can prevent ice crystal formation in ice cream, thicken jam, and improve the mouthfeel in dairy products.
2. Replacing Animal-Based Gum
Locust bean gum is a plant-derived colloid suitable for vegetarian or religious products (for example, replacing gelatin in vegan soft candies).
3. Extending the Shelf Life of Foods
Locust bean gum extends the shelf life of baked goods, sauces, and other products by locking in moisture and inhibiting ingredient separation.

Specific Food Applications of Locust Bean Gum
In the food industry, locust bean gum is commonly used as a thickener, water-binding agent, adhesive, and gelling agent. It can be used in jelly, ice cream, canned pet food, dairy products, cheese, meat products, puffed foods, pasta products, and baked fillings.
1. Dairy Products
In dairy products such as yogurt and cheese, locust bean gum can control viscosity, prevent syneresis, and enhance the product's texture, making it smoother and more stable, thereby extending shelf life. For example, adding an appropriate amount of locust bean gum to yogurt can effectively reduce whey precipitation and improve the product's sensory quality.



2. Frozen Foods
In frozen foods such as ice cream and popsicles, locust bean gum can control ice crystal growth, improve the product's resistance to melting, and create a smoother and denser texture. Ice cream with locust bean gum can better maintain its shape and texture during storage and distribution.
3. Baked Goods
In baked goods such as bread and cakes, locust bean gum can enhance the dough's air retention, increase its volume and softness, and slow starch aging, extending its shelf life. Bread with locust bean gum retains its excellent taste and freshness even after several days.

4. Other Foods
LBG Locust bean gum can also be used in meat products, sauces, canned foods, and other foods to thicken, stabilize, and improve texture. In canned meat sauce, locust bean gum can make the meat sauce texture uniform and prevent oil and water from separating.
What Are The Chemical Properties Of LBG Locust Bean Gum?
1. Water Solubility
At room temperature, locust bean gum has only limited solubility in water. Heating the solution hydrates the gum, improving its properties. Heating at 80°C for 10 minutes results in complete hydration. Upon cooling, locust bean gum remains free and extended in solution, making it useful as a thickener or chemical reagent. This property is explained by the distribution of side chain branches. Here, mannose residues on the main chain contact and strongly bond with mannose residues on adjacent chains. Sufficient heat is required to break these intermolecular bonds. Water is a common solvent, but aqueous solutions of locust bean gum can tolerate limited concentrations of water-miscible solvents (such as ethanol). Like most other polymers, locust bean gum is also soluble in dimethylformamide and dimethyl sulfoxide.
Commercial locust bean gum solutions are generally turbid, largely due to the presence of the endosperm. Locust bean gum, carefully purified in the laboratory using non-industrial methods, can produce solutions with clarity similar to that of water.
2. Rheological Properties
Among water-soluble gums, locust bean gum is one of the most effective water-soluble thickeners. Its solutions are non-Newtonian (pseudoplastic) fluids. These solutions thin reversibly when heated, but will irreversibly degrade if heated at a constant temperature for extended periods. Like other water-soluble polymers, locust bean gum solutions are resistant to shear degradation, but will gradually degrade under high shear forces.
LBG Locust Bean Gum Viscosity
1. Effect of concentration on viscosity
LBG Locust bean gum has unusual properties. A 1% solution of unmodified locust bean gum is thick, and at a concentration of 3%, it resembles a gel rather than a solution. The viscosity of locust bean gum increases with concentration, reaching 46.4 mPa·s at a concentration of 2%.
2. Effect of Temperature on Viscosity
Heating below 80°C can increase the viscosity of locust bean gum solutions, with 60°C being the optimal heating temperature. Ordinary locust bean gum is only partially soluble in cold water and requires heating to 85°C for at least 10 minutes to fully hydrate, reaching its maximum viscosity upon cooling.

Effect of temperature on viscosity
3. Effect of pH on Viscosity
pH has little effect on the viscosity of locust bean gum solutions. Within a pH range of 3.5-9, the viscosity remains essentially unchanged, but outside this range, the viscosity decreases. Locust bean gum is also relatively stable in alkaline solutions. This property makes it widely applicable.
4. Effect of Freeze-Thaw Cycles on Viscosity
Freezing has no effect on the viscosity of locust bean gum solutions, but refrigeration can reduce the viscosity of locust bean gum.
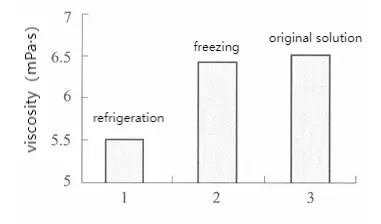
Effect of freeze-thaw cycles on viscosity
As a professional LBG locust bean gum manufacturer and supplier, YTBIO is committed to providing high-quality LBG locust bean gum to every customer. We have a professional team and our own production plant. If you have any questions or needs, please contact us and we will respond as soon as possible.
_1737093401309.png)

