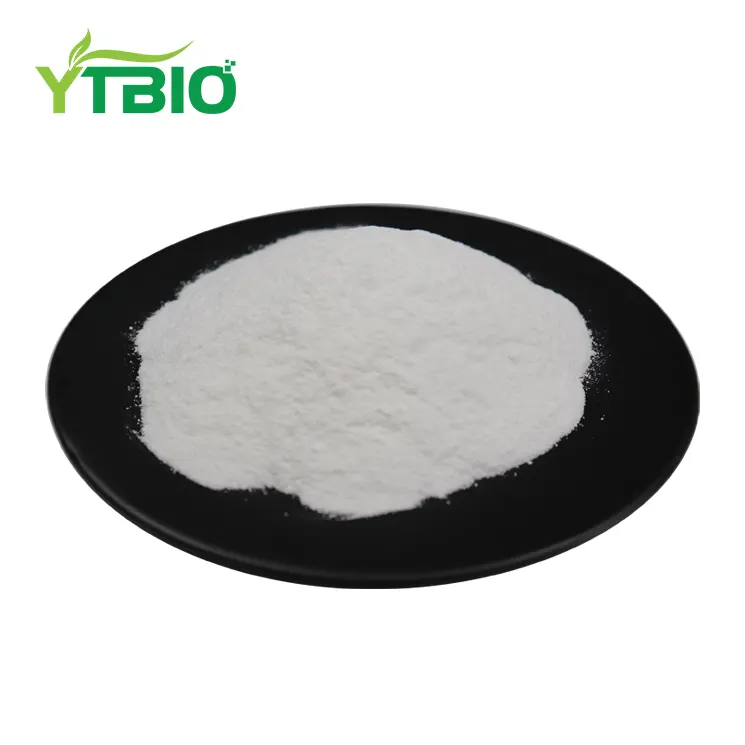
Oxymatrine Powder
Specification: 98% Oxymatrine
Test method: HPLC
Appearance: White Powder
Shelf Life: 2 years
Application: Food,Health product addition, Dietary
Storage conditions: This product should be sealed and shaded, stored in a dry
Certifications:ISO9001,ISO22000,Kosher,Halal,HACCP
Shipping speed:1-3 days
- Fast Delievery
- Quality Assurance
- 24/7 Customer Service
Product Introduction
What is oxymatrine powder?
Oxymatrine is a natural alkaloid that mainly exists in Sophor flavescens Ait., S. tonkinensis Gagnep, S. alopecuroides L. and S. viciifolia. Hance. A large number of studies have found that oxymatrine can resist the damage to vascular endothelial cells caused by hypoxia, high sugar and bacterial toxins, inhibit vascular endothelial-mesenchymal transition, and can also resist hypoxia, transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), Hyperlipidemia induces vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and β-glycerophosphate damages vascular smooth muscle cells, thereby producing vascular protection and improving vascular function. Oxymatrine can dilate blood vessels and resist the contracture effects of high sugar, high fat, and phenylephrine on blood vessels; it can block and promote the synthesis and release of nitric oxide through ganglia, produce antihypertensive effects, and can also regulate cardiac function by improving Blood pressure; can inhibit pulmonary arterial hypertension and pulmonary vascular remodeling caused by hypoxia or monocrotaline in rats, as well as atherosclerosis caused by high-fat diet.

What are the effects of oxymatrine?
1. Protect umbilical vein endothelial cells
In an in vitro experiment to study the anti-tumor angiogenesis of oxymatrine, human umbilical vein endothelial cells were used as a control. The results showed that the half inhibitory concentration (IC50) of oxymatrine in inhibiting the proliferation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells was 1555 mg/L. , can make cell nuclei deeply stained, cell volume smaller and irregular, extracellular villi reduced, most of them in an early apoptosis state, and can significantly inhibit the activity of succinate dehydrogenase in aerobic oxidation. Oxymatrine can concentration-dependently improve the low survival rate of human umbilical vein endothelial cells caused by hypoxia and reoxygenation, reduce the lactate dehydrogenase content in the culture medium, and increase the Bcl-2/Bax ratio and down-regulate caspases. -3 protein expression. Another study reported that oxymatrine did not affect the proliferation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells when the concentration was 1 and 3 μmol/L, but inhibited its proliferation when it was 10 and 30 μmol/L; 3 μmol/L can resist the effects of high glucose on human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Damage and decreased activity of endothelial cells; expression of A2B receptors and independent chemokine CCL5 receptors that can resist high glucose upregulation of adenosine, as well as phosphorylation of p38 and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/(2 ERK1/2) , indicating that the mechanism is that oxymatrine resists the damage of endothelial cells caused by high glucose by down-regulating the expression of A2B receptors.
2. Protect arterial and microvascular endothelial cells
Oxymatrine can promote endothelial cell proliferation at low concentrations, and its mechanism is related to inhibiting the secretion of vascular endothelial growth factors by tumor cells and downregulating the expression of growth factor receptors related to blood vessels. Studies have reported that intraperitoneal injection of oxymatrine 120 mg/kg for 10 consecutive days can reduce the protein expression of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), ERK1/2, p38MAPK and JNK in basilar artery endothelial cells in rats with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Gene expression of interleukin (LT)-1β, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α). The relevant mechanism is related to down-regulating the expression of A2B receptors, blocking the MAPK/ERK/JNK signaling pathway, and inhibiting inflammatory responses. In addition, oxymatrine can inhibit endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition, protect vascular endothelial cells, and inhibit vascular remodeling by downregulating the expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α.
3. Protect blood vessels and inhibit angiogenesis
Research reports that intraperitoneal injection of 100 mg/kg of oxymatrine into pulmonary fibrosis model rats injected with bleomycin for 27 consecutive days can significantly reduce alveolitis and fibrocollagen tissue hyperplasia in the lung interstitium of the model rats. In the early stage of pulmonary fibrosis, it can significantly resist bleomycin and increase the density of pulmonary microvessels. Its mechanism is related to inhibiting the formation of new blood vessels in the early stage of pulmonary fibrosis, correcting the imbalance of Th1/Th2, and inhibiting collagen synthesis.
4. Improve vasoconstriction and relaxation function to regulate blood pressure
Oxymatrine has anti-inflammatory effects, can protect vascular endothelial cells, and alleviate cerebral vasospasm in rats with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Intravenous injection of oxymatrine 4 mg/kg into anesthetized mice can significantly increase the caliber, flow rate and flow rate of the mouse meningeal microvessels, indicating that oxymatrine can not only expand microvessels, but also enhance the amplitude and frequency of microarterial autonomic movements and activate The autonomous movement of arterioles in an inhibited state regulates microvascular function and prevents blood cell aggregation, thereby redistributing local blood flow and improving blood perfusion and blood oxygen exchange. Type 2 diabetic rats established by feeding high sugar and high fat combined with injection of low-dose streptozotocin for 4 consecutive weeks can significantly increase the diastolic percentage of the thoracic aorta of the model rats and reduce the The elevated gene expression of A2B receptors in the aorta significantly reduced the average blood pressure, systolic blood pressure, and diastolic blood pressure of the model rats, and this dose did not affect the fasting and postprandial blood glucose of the model rats.
5. Anti-pulmonary hypertension effect
Monocrotaline was used to create a rat pulmonary arterial hypertension model, and oxymatrine was administered intragastrically to the model rats for 28 consecutive days. It can significantly reduce the lung index and right ventricular hypertrophy of the model rats, and improve the right ventricular systolic function (reduce the right ventricular systolic pressure). , the maximum change rate of right ventricular intraventricular pressure), does not affect heart rate, and reverses right ventricular hypertrophy; it can reduce serum cardiac troponin-I levels in rats with pulmonary hypertension, improve the structure of small and medium pulmonary arteries, reduce wall thickness, and lumen The area is enlarged, inflammatory cell infiltration is reduced, pulmonary arteriole remodeling is improved, pulmonary artery vascular resistance is reduced, peripheral resistance of the entire pulmonary circulation is reduced, pulmonary artery pressure is reduced, right ventricular afterload is reduced, and right ventricular failure is reversed. Research on the mechanism of action found that oxymatrine can reduce the serum ADMA level in model rats, up-regulate the protein expression of protein kinase B (Akt) and phosphorylated Akt in lung tissue, reaching the level of normal rat lung tissue; it can up-regulate eNOS in lung tissue and phosphorylated eNOS and the expression of dimethylarginine dimethylamine hydrolase-2 (DDAH2). Since it does not affect the expression of protein arginine methyltransferase-1, it is believed that oxymatrine promotes Akt/ The eNOS signaling pathway and the up-regulation of DDAH2 expression in lung tissue promote the catabolism of ADMA, a competitive inhibitor of eNOS, restore and accelerate the synthesis of NO, and produce anti-pulmonary hypertension effects.
What are the market applications of oxymatrine?
Medical uses: In the pharmaceutical field, matrine is used as an anti-tumor drug, and studies have shown that it has an inhibitory effect on certain cancer cells. In addition, matrine is also used to treat rheumatic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Cosmetics and health products: Matrine is also added to some cosmetics and health products and is said to have antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects.
Test report on oxymatrine
Items & Results | ||
Item | Spec. | Result |
Appearance | Light yellow to white powder | Conforms |
Odor | Characteristic | Conforms |
Taste | Characteristic | Conforms |
Particle Size | 98% Through 80 Mesh | Conforms |
Dihydromyricetin | ≥98% | 98.67% |
Loss on Drying | ≤5.0% | 0.24% |
Ash | ≤1.0 % | 0.31% |
Total Heavy Metals | ≤10 ppm | Conforms |
Pesticides | Negative | Conforms |
Solvent residences | ≤0.01% | Conforms |
Total Plate Count | ≤1,000 cfu/g | Conforms |
Moulds&Yeast | ≤100 cfu/g | Conforms |
Escherichia Coli | Negative | Conforms |
Salmonella | Negative | Conforms |
Conclusion | Conform to Enterprise standard | |
Certificates
YTBIO is committed to providing customers with the highest-quality Pure Oxymatrine Powder bulk and services so that every consumer can enjoy natural, healthy, and high-quality food. If you have any inquiries or needs about our products, please feel free to contact us, and we will reply to you as soon as possible.

Package & Shipment


Our Company and Factory

_1737093401309.png)

