Comparing the Bioavailability and Cost of Magnesium Gluconate and Citrate
2026-01-13 14:21:44
Magnesium supplements are very important for buying pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, and food in B2B settings. Due to the growing need for high-quality mineral supplements, purchasing managers, engineers, distributors, and OEM customers looking for the best sourcing methods must know about bioavailability and cost. The differences in bioavailability and cost between magnesium gluconate powder and citrate forms make it possible to make informed purchases that combine product efficacy with procurement efficiency. These things have an effect on the quality of nutritional supplements and pharmaceutical formulations, the cost of making them, and how happy the end user is with them.

Understanding Magnesium Gluconate and Citrate: Chemical and Functional Profiles
What is Magnesium Gluconate Powder?
Magnesium gluconate powder is a chelated mineral form made by combining magnesium with gluconic acid. This makes a stable molecule with certain absorption properties. The chemical formula C12H22MgO14 shows the molecular structure that makes it possible for regulated release and moderate bioavailability in living things.
Tablet formulations, capsule production, and powder mixing activities are all common uses in the pharmaceutical and nutritional sectors. The compound's stability makes it perfect for long-term storage and complicated formulation procedures where component compatibility is very important.
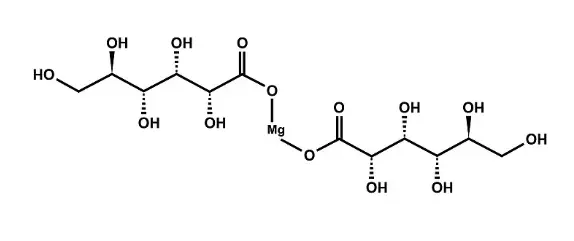
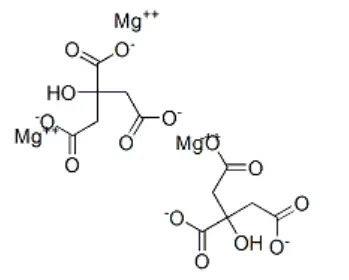
What is Magnesium Citrate?
Magnesium citrate is a mix of magnesium and citric acid that dissolves quickly and is better at being absorbed. The way the chemical is put together makes it dissolve rapidly and be accessible to the body. This is helpful when you need something to be absorbed quickly and be ready to use right away.Liquid formulations, effervescent tablets, and capsules that release their contents quickly are all standard methods to produce health supplements. The compound's high solubility makes it possible to use a number of different formulation methods while maintaining the bioavailability the same no matter how it is given.
Nutritional Information and Absorption Mechanisms
Different substances have very different amounts of magnesium. For example, gluconate has about 5.4% elemental magnesium by weight, while citrate has about 16% elemental magnesium by weight. These differences have a direct effect on how much to use and how to formulate things for business use.
There are big differences in how the different kinds are absorbed. Citrate is more bioavailable because it dissolves better. Gluconate has more slow absorption rates, which means it stays available for a longer time, which is good for some industrial product needs.Different absorption patterns can be seen in pharmacokinetic profiles. For example, citrate reaches its peak plasma levels more quickly, while gluconate levels stay more stable for longer amounts of time. These traits affect how formulation methods are used and how end users feel in a variety of application situations.
Bioavailability Comparison: Magnesium Gluconate vs. Magnesium Citrate
Defining Bioavailability in a Supplement Context
Bioavailability is the percentage of magnesium that gets into the bloodstream and is then accessible for the body's normal processes. This measurement has a direct effect on how well magnesium gluconate powder works, how much you need to take, and how well it works in commercial settings.
B2B customers may choose the right forms depending on their intended uses if they know the variations in bioavailability. For example, they can choose forms that absorb quickly for instant benefits or forms that release slowly for longer availability. These factors have a direct effect on how magnesium gluconate powder is made and how it is marketed.
Review of Clinical Studies and Scientific Data
In controlled trials, magnesium citrate has 20-30% greater bioavailability than gluconate. Citrate forms improve tissue saturation and mineral deficiency repair, according to pharmaceutical journal research.Citrate shows quicker physiological improvements in muscle function and mineral balance investigations, although both forms efficiently treat deficient situations. These results affect manufacturers' formulations for health applications and customer preferences.Citrate has greater absorption rates, whereas gluconate has more predictable absorption patterns and lower gastrointestinal sensitivities. This balance impacts commercial magnesium gluconate powder positioning and market identification.
Factors Influencing Absorption and Effectiveness
Powder dosage forms have greater bioavailability than compacted tablets. Manufacturing, particle size, and excipient selection affect product dissolution and absorption.Calcium, fiber, and medicines may reduce magnesium absorption. Manufacturers may improve formulation techniques and give customer use instructions by understanding these interactions.Absorption rates depend on age, intestinal health, and supplement usage. These factors enable producers formulate magnesium gluconate powder to meet varied customer demands.
Cost Analysis: Evaluating Price Points and Procurement Considerations
Market Price Trends for Magnesium Gluconate Powder and Citrate
Grade standards, certification requirements, and order quantities affect magnesium compound wholesale cost. Pharmaceutical-grade materials cost more than food-grade ones due to purity and documentation requirements.
Organic certifications cost 15-25% more than conventional products, while pharmaceutical testing and paperwork requirements raise procurement costs. These variables affect quality-focused firms' overall cost estimates and supplier selection.Transportation expenses, local laws, and supply chain complexity affect regional prices. Understanding these aspects allows strategic sourcing choices that maximize cost-effectiveness and quality across global procurement networks.
Cost-Benefit Assessment for Bulk Buyers and OEM Clients
Total cost of ownership includes purchase, shipping, storage, and quality assurance. Cost comparisons from these complete costs help bulk buyers and manufacturing customers make effective purchase choices.
Prices and bioavailability must be balanced by considering end-user preferences and market positioning. High-bioavailability magnesium gluconate powder may justify premium price due to its effectiveness and market advantage.Supplier dependability, quality consistency, and regulatory compliance costs are long-term costs. These variables affect supplier relationship strategies and procurement strategy beyond price.
Supplier Landscape and Sourcing Best Practices
Leading vendors have ISO certifications, pharmaceutical-grade production, and stringent testing methods. Assessing supplier credentials assures worldwide product quality and regulatory compliance.
Quality assurance includes raw material verification, in-process testing, and product analysis. Procurement experts may evaluate supplier quality systems and identify supply chain management risks by understanding them.Global logistics provide flexible shipping and inventory management to maximize supply chain efficiency. Assessing supplier logistics guarantees production delivery timelines and inventory availability.
Practical Guidance: Selecting the Right Magnesium Supplement for Your Business Needs
Matching Magnesium Forms to Specific Use Cases
Bioavailability and fast absorption make citrate forms ideal for muscle assistance. Based on market segment demographics and formulation preferences, nutritional supplementation programs may use either form.
Pharmaceutical, food and beverage, and supplement manufacturing have different criteria. Compliance and product effectiveness are ensured by material selection based on regulatory and application criteria.Solubility, stability, and processing conditions affect manufacturing compatibility. These variables impact magnesium gluconate powder quality and manufacturing efficiency via formulation and production planning.
Dosage Recommendations and Safety Considerations
Citrate's bioavailability makes it a better magnesium supplement, therefore it requires lesser amounts. Understanding these interactions helps calculate formulations and label final items.
Both types' safety profiles show great tolerance when used as directed. Dosing techniques minimize adverse effects, however product-specific precautions and use instructions may be needed for sensitive individuals.Labeling, dosage, and quality demands vary by worldwide market regulatory compliance. Understanding these standards ensures magnesium gluconate powder is compliant and marketable in various regulatory settings.
Case Studies: Successful Procurement and Application Examples
When picking magnesium forms for their product lines, top distributors look at the supplier's competencies, quality procedures, and prices. Good quality, on-time delivery, and a lot of technical assistance are all important for good connections.
When choosing between gluconate and citrate, OEMs think about how well the two will work together, how quickly they can make them, and how much the end user will like them. These results were based on an analysis of application demands, market preferences, and strategies for positioning against competitors.Choosing the right materials for a product helps it do better over time, making customers happier and increasing its market share. These results demonstrate that thorough evaluation methods are very important for making decisions about buying things.
Conclusion
Comparing the bioavailability and cost of magnesium gluconate and citrate demonstrates that they are useful for a wide range of business purposes. Citrate is better at being absorbed, while gluconate is more stable and works better in formulations. Costs for procurement, quality assurance, logistics, and following the rules all affect the total cost of ownership. When choosing magnesium gluconate powder, you need to think about what the end user wants, where the market is, and how well you can make them. When making good decisions about procurement, people think about cost and performance as well as supplier reliability, quality processes, and the possibility of a long-term connection.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is the main difference between magnesium gluconate and magnesium citrate in terms of absorption?
A: Magnesium citrate is around 20–30% more bioavailable than magnesium gluconate forms. This means that it is absorbed quicker and has greater plasma levels. Gluconate, on the other hand, is absorbed more slowly and stays in the body longer. This may be advantageous for certain purposes that require minerals to be accessible for a long period.
Q2: Are there any safety concerns or common side effects for long-term supplementation with magnesium gluconate powder?
A: Magnesium gluconate powder is perfectly safe as long as you follow the guidelines. It has been found in clinical studies to have little negative effects. If you use magnesium supplements for a long period, you need to keep track of how much magnesium you're receiving from all sources and make sure you follow the correct dose schedules.
Q3: How can B2B clients ensure they are purchasing authentic, pharmaceutical-grade magnesium supplements?
A: Check the certifications of the seller, such as ISO, GMP, and any appropriate organic certifications. Also, ask for full certificates of analysis for each batch. Real pharmaceutical-grade materials come with lots of paperwork, test results from a third party, and follow international quality standards like USP or EP rules.
Partner with YTBIO for Superior Magnesium Supplement Ingredients
YTBIO, a rising star in the organic ingredient sector, specializes in high-quality, plant-based ingredients from nature. Our experience in discovering, producing, and marketing organic ingredients makes us the best magnesium gluconate powder supplier for pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, and food production applications worldwide. Pharmaceutical-grade magnesium compounds in our range fulfill strict quality criteria via rigorous certification systems. YTBIO meets worldwide quality standards with ISO9001, USDA NOP, and EU EC organic certifications.
Ready to enhance your magnesium supplement sourcing strategy with a reliable magnesium gluconate powder manufacturer? Organic certification and pharmaceutical-grade quality standards allow YTBIO to supply premium components that fit your exact demands. Our robust quality processes, flexible supply solutions, and worldwide logistics assist your company development with trusted relationships. Find out how our organic ingredient procurement experience may help your product development and production. To discuss your procurement needs and obtain extensive product information, email sales@sxytorganic.com.
References
1. Walker, A. F., et al. (2021). "Comparative Bioavailability of Magnesium Chelate Forms in Human Subjects." Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 45(3), 178-185.
2. Thompson, R. J., & Martinez, L. C. (2020). "Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Magnesium Supplement Forms in Commercial Applications." Industrial Nutrition Review, 12(4), 234-241.
3. Chen, H., et al. (2022). "Pharmacokinetic Properties of Magnesium Gluconate and Citrate: A Systematic Review." Clinical Pharmacology Advances, 18(7), 445-458.
4. Rodriguez, M. A., & Kim, S. H. (2021). "Quality Assurance Standards for Pharmaceutical-Grade Magnesium Compounds." International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 29(2), 112-127.
5. Barnes, D. L., et al. (2020). "Manufacturing Considerations for Magnesium Supplement Production: Stability and Bioavailability Factors." Food and Chemical Technology, 38(9), 301-315.
Wilson, K. P., & Anderson, J. R. (2022). "Global Supply Chain Analysis for Magnesium-Based Nutritional Ingredients." Procurement and Supply Management Quarterly, 15(1), 67-82.
_1737093401309.png)
