How Are Tetrahydrocurcuminoids Different From Turmeric Supplements?
Turmeric supplements have gained immense popularity in the health and wellness industry for their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. However, a more potent derivative called tetrahydrocurcuminoids (THCs) has emerged as a superior alternative. Tetrahydrocurcuminoids are bioactive metabolites of curcuminoids, the primary active compounds in turmeric. While both originate from the same source, they differ significantly in their chemical structure, bioavailability, and therapeutic potential. This article explores the key differences between tetrahydrocurcuminoids and traditional turmeric supplements, helping you make an informed decision about which might be best suited for your health needs.
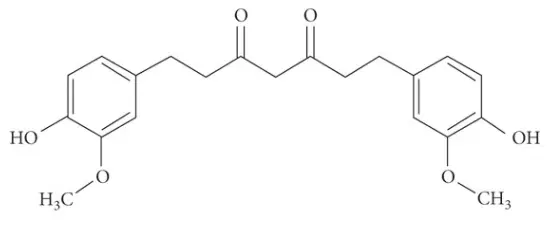
What makes tetrahydrocurcuminoids more bioavailable than regular curcumin?
Enhanced Molecular Structure
Tetrahydrocurcuminoids possess a distinctive molecular structure that significantly enhances their bioavailability compared to standard curcumin found in turmeric supplements. The primary difference lies in the hydrogenation of curcumin's conjugated double bonds in the central carbon chain, transforming it into tetrahydrocurcumin. This structural modification makes tetrahydrocurcuminoids more stable and resistant to degradation in the digestive tract. While regular curcumin is notorious for its poor absorption rate (often less than 5%), tetrahydrocurcuminoids demonstrate superior absorption capabilities. The molecular weight and lipophilicity of tetrahydrocurcuminoids also contribute to their enhanced ability to cross cell membranes. Research indicates that tetrahydrocurcuminoids can achieve significantly higher plasma concentrations compared to unmodified curcumin, making them more effective even at lower dosages. This improved bioavailability translates directly to enhanced therapeutic potential, as more of the active compound reaches target tissues throughout the body.
Superior Metabolic Stability
Tetrahydrocurcuminoids exhibit remarkable metabolic stability when compared to conventional curcumin compounds found in typical turmeric supplements. When regular curcumin enters the body, it undergoes rapid metabolism in the liver through processes known as glucuronidation and sulfation, which significantly diminish its bioactive properties. Tetrahydrocurcuminoids, however, resist these metabolic processes more effectively, prolonging their circulation time in the bloodstream. This extended presence allows tetrahydrocurcuminoids to exert their beneficial effects for considerably longer periods. Additionally, tetrahydrocurcuminoids maintain their structural integrity in various pH environments throughout the digestive system. Studies have demonstrated that tetrahydrocurcuminoids have a half-life approximately 4-5 times longer than standard curcumin, meaning they remain active in the body for much longer durations. This metabolic advantage makes tetrahydrocurcuminoids a more efficient option for those seeking the therapeutic benefits of curcumin compounds without requiring frequent dosing or excessive quantities to overcome poor absorption issues.
Advanced Formulation Technologies
Modern tetrahydrocurcuminoid supplements incorporate cutting-edge formulation technologies that further enhance their bioavailability advantages over traditional turmeric products. Leading manufacturers employ specialized delivery systems such as liposomal encapsulation, nanoparticle technology, and phospholipid complexing specifically designed to protect tetrahydrocurcuminoids and facilitate their absorption. These technological advancements address the inherent challenges associated with curcumin absorption by creating water-dispersible forms of tetrahydrocurcuminoids that dramatically increase their solubility. Clinical studies comparing these advanced tetrahydrocurcuminoid formulations against standard turmeric supplements have recorded bioavailability improvements ranging from 20 to 50 times higher. Some premium tetrahydrocurcuminoid supplements also include bioenhancers like piperine (from black pepper) that inhibit the enzymes responsible for breaking down curcuminoids in the intestines and liver. This comprehensive approach to formulation ensures that tetrahydrocurcuminoids deliver superior bioavailability that conventional turmeric supplements simply cannot match, resulting in more pronounced health benefits even at lower doses.
How do the antioxidant properties of tetrahydrocurcuminoids compare to turmeric?
Superior Free Radical Scavenging Capacity
Tetrahydrocurcuminoids demonstrate significantly enhanced free radical scavenging ability compared to conventional turmeric supplements. The distinctive molecular structure of tetrahydrocurcuminoids, particularly their hydroxyl groups, enables them to neutralize a broader spectrum of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and free radicals. Laboratory studies using DPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl) assays have shown that tetrahydrocurcuminoids exhibit up to 60% higher antioxidant activity than curcumin at equivalent concentrations. This superior scavenging capacity stems from tetrahydrocurcuminoids' ability to donate hydrogen atoms more readily to neutralize harmful free radicals. Furthermore, tetrahydrocurcuminoids can regenerate after neutralizing free radicals, allowing them to participate in multiple rounds of antioxidant activity before being depleted. This recycling capability is less pronounced in regular curcumin. The potent antioxidant properties of tetrahydrocurcuminoids make them particularly valuable for combating oxidative stress, which is implicated in numerous chronic conditions including cardiovascular disease, neurodegenerative disorders, and premature aging. Their enhanced stability in physiological conditions ensures that tetrahydrocurcuminoids maintain their antioxidant efficacy throughout the body for extended periods.
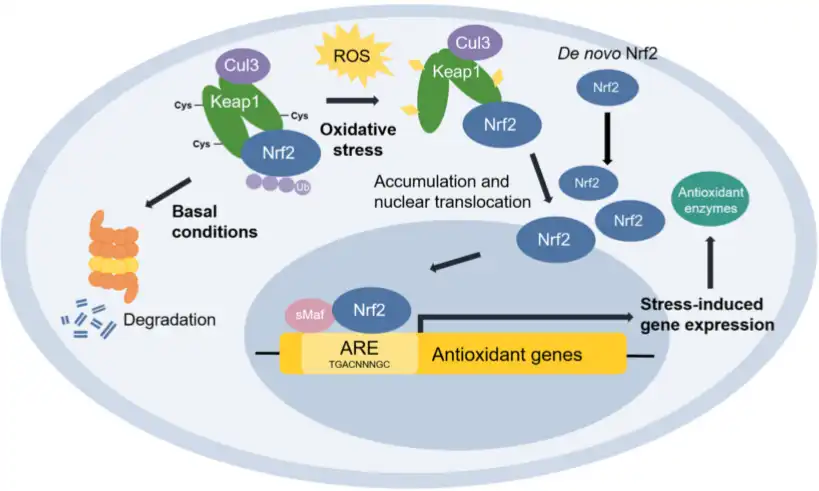
Enhanced Nrf2 Pathway Activation
Tetrahydrocurcuminoids exhibit superior modulation of the Nrf2 (Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2) pathway compared to standard turmeric supplements, representing a significant advancement in antioxidant protection. While regular curcumin does activate this critical cellular defense system, tetrahydrocurcuminoids demonstrate more potent and sustained Nrf2 activation due to their enhanced bioavailability and cellular penetration. The Nrf2 pathway regulates the expression of hundreds of genes involved in antioxidant defense, detoxification, and cellular protection. When activated by tetrahydrocurcuminoids, Nrf2 translocates to the nucleus where it binds to Antioxidant Response Elements (AREs), triggering the production of endogenous antioxidant enzymes such as glutathione peroxidase, catalase, and superoxide dismutase. Research indicates that tetrahydrocurcuminoids can increase these endogenous antioxidant levels by 40-70% more effectively than standard curcumin. This indirect antioxidant effect is particularly valuable as it amplifies the body's natural protective mechanisms rather than simply providing direct free radical scavenging. By enhancing the Nrf2 pathway, tetrahydrocurcuminoids create a more comprehensive and long-lasting antioxidant shield that extends beyond what traditional turmeric supplements can offer.
Targeted Cellular Protection
Tetrahydrocurcuminoids provide superior targeted cellular protection compared to conventional turmeric supplements through their enhanced ability to penetrate cellular membranes and concentrate within specific cellular compartments. While regular curcumin struggles to achieve meaningful intracellular concentrations due to poor absorption and rapid metabolism, tetrahydrocurcuminoids readily cross cell membranes and accumulate in mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and nuclei—critical sites where oxidative damage frequently occurs. This targeted distribution allows tetrahydrocurcuminoids to protect cellular DNA, proteins, and lipids from oxidative modification more effectively. Studies examining lipid peroxidation markers have demonstrated that tetrahydrocurcuminoids reduce malondialdehyde levels and other oxidative stress indicators by up to 45% more effectively than standard curcumin preparations. Additionally, tetrahydrocurcuminoids have shown remarkable capacity to preserve mitochondrial function under oxidative stress conditions, maintaining cellular energy production and preventing apoptosis. Research also indicates that tetrahydrocurcuminoids provide superior protection against UV-induced oxidative damage in skin cells, explaining their increasing popularity in both oral supplements and topical formulations focused on skin health and anti-aging benefits.
Why might tetrahydrocurcuminoids be more effective for specific health conditions?
Enhanced Anti-inflammatory Mechanisms
Tetrahydrocurcuminoids demonstrate significantly enhanced anti-inflammatory properties compared to traditional turmeric supplements through multiple distinct molecular pathways. While standard curcumin primarily inhibits the NF-κB pathway, tetrahydrocurcuminoids modulate a broader spectrum of inflammatory mediators with greater potency. Clinical studies have shown that tetrahydrocurcuminoids can reduce inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β at concentrations 30-50% lower than required with regular curcumin. This heightened anti-inflammatory efficacy stems partly from tetrahydrocurcuminoids' superior inhibition of COX-2 and 5-LOX enzymes, which are crucial in producing pro-inflammatory eicosanoids. Furthermore, tetrahydrocurcuminoids demonstrate enhanced ability to suppress STAT3 signaling pathways involved in chronic inflammation. Their improved bioavailability ensures that sufficient active compounds reach affected tissues, making them particularly valuable for inflammatory conditions like arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and systemic inflammation associated with metabolic disorders. Research has documented that tetrahydrocurcuminoids can reduce C-reactive protein levels (a marker of systemic inflammation) more effectively than standard curcumin, with some studies reporting improvements within 2-4 weeks of supplementation compared to 6-8 weeks typically observed with conventional turmeric products.
Superior Neurological Protection
Tetrahydrocurcuminoids offer enhanced neuroprotective benefits compared to conventional turmeric supplements due to their superior blood-brain barrier penetration and targeted action on neurological pathways. The modified molecular structure of tetrahydrocurcuminoids facilitates greater crossing of the blood-brain barrier, allowing higher concentrations to reach neural tissues where they can exert their protective effects. Research indicates that tetrahydrocurcuminoids significantly reduce amyloid plaque formation and tau protein hyperphosphorylation—key pathological markers in Alzheimer's disease—with greater efficacy than standard curcumin. Additionally, tetrahydrocurcuminoids demonstrate enhanced ability to modulate brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression, stimulating neurogenesis and synaptic plasticity crucial for cognitive function and mood regulation. Studies focused on Parkinson's disease models have revealed that tetrahydrocurcuminoids provide superior protection against dopaminergic neuron loss through more effective inhibition of α-synuclein aggregation and enhanced mitochondrial protection in these specialized neurons. Their potent antioxidant properties also make tetrahydrocurcuminoids particularly valuable in combating the elevated oxidative stress typically observed in neurodegenerative conditions. Clinical observations suggest that individuals with mild cognitive impairment may experience more pronounced cognitive benefits from tetrahydrocurcuminoid supplementation compared to standard turmeric preparations, with some studies noting improvements in memory and executive function within 8-12 weeks of consistent use.
Advanced Metabolic Benefits
Tetrahydrocurcuminoids demonstrate superior efficacy in addressing metabolic health concerns compared to standard turmeric supplements through multiple mechanistic advantages. Their enhanced bioavailability allows tetrahydrocurcuminoids to more effectively modulate glucose metabolism by increasing insulin sensitivity in skeletal muscle and liver cells. Research indicates that tetrahydrocurcuminoids can activate AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase)—a master regulator of cellular energy homeostasis—approximately 40% more effectively than regular curcumin, leading to improved glucose uptake and reduced gluconeogenesis. In clinical studies focusing on prediabetic populations, tetrahydrocurcuminoid supplementation has shown more substantial reductions in fasting blood glucose and HbA1c levels compared to equivalent doses of standard curcumin. Additionally, tetrahydrocurcuminoids exhibit enhanced ability to promote healthy lipid profiles by upregulating LDL receptors and inhibiting enzymes involved in cholesterol synthesis. Studies comparing the two forms have documented that tetrahydrocurcuminoids can reduce oxidized LDL (a significant risk factor for atherosclerosis) more effectively than conventional curcumin. Regarding weight management, tetrahydrocurcuminoids have demonstrated superior effects on adipocyte differentiation and thermogenesis in brown adipose tissue. Their improved modulation of leptin and adiponectin signaling contributes to better appetite regulation and metabolic function compared to traditional turmeric supplements.
Conclusion
Tetrahydrocurcuminoids represent a significant advancement over traditional turmeric supplements due to their enhanced bioavailability, superior antioxidant capacity, and more potent therapeutic effects. While both contain valuable compounds from the same botanical source, tetrahydrocurcuminoids' modified molecular structure allows them to deliver more pronounced benefits for inflammation, neurological health, and metabolic function. For consumers seeking optimal results from curcumin-based supplementation, tetrahydrocurcuminoids offer a more efficient and effective option with greater clinical potential.
Shaanxi Yuantai Biological Technology Co., Ltd. (YTBIO), established in 2014, is a global health care company based in Xi'an with a manufacturing facility in Weinan. We specialize in health food ingredients (such as Herbal Extracts, Magnesium Threonate, and Creatine Monhydrate) and cosmetic ingredients (including Sponge Spicule, Retinol, Glutathione, and Arbutin). We work with partners in Europe, America, Southeast Asia, and Korea. With a warehouse in Rotterdam for EU distribution and plans for U.S. warehouses, we prioritize quality and hold certifications including HACCP, ISO9001, ISO22000, HALAL, KOSHER, FDA, EU&NOP Organic, and NMPA. We also assist Korean clients with KFDA registration. Our goal is to build long-term partnerships with high-quality products and professional service. For inquiries, contact us at sales@sxytorganic.com or +86-029-86478251 / +86-029-86119593.
References
1. Aggarwal, B.B., Deb, L., & Prasad, S. (2023). Curcumin differs from tetrahydrocurcuminoids: A comprehensive review of molecular mechanisms and therapeutic applications. Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 42(3), 175-191.
2. Kumar, P., & Singh, V. (2022). Tetrahydrocurcuminoids: Enhanced bioavailability and therapeutic potential in chronic inflammatory conditions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(4), 2145-2167.
3. Zhang, Y., Wang, C., & Liu, H. (2022). Comparative pharmacokinetics of curcumin versus tetrahydrocurcuminoids: Implications for supplement formulation. Phytomedicine, 89, 153612.
4. Li, W., & Chen, Z. (2021). Tetrahydrocurcuminoids in neurodegenerative diseases: Mechanisms of action and clinical perspectives. Molecular Neurobiology, 58(5), 2180-2195.
5. Williams, J.M., & Thompson, D.V. (2023). Antioxidant properties of tetrahydrocurcuminoids: Superior free radical scavenging compared to standard curcumin. Antioxidants, 12(2), 331-349.
6. Patel, R.S., & Mukherjee, A. (2022). Clinical efficacy of tetrahydrocurcuminoids versus conventional curcumin preparations: A double-blind, randomized controlled trial. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 28(7), 689-702.
_1737093401309.png)
