How Does Microcrystalline Cellulose Act as a Bulking Agent in Pills?
2025-08-25 11:16:10
Making drugs that are both easy to take and effective is a never-ending task for the pharmaceutical industry. The multipurpose ingredient microcrystalline cellulose powder (MCC), which is essential to the formation of pills, is one of the unsung heroes in this process. This article explores the benefits of MCC and how it works as a bulking agent in tablets, contrasting it with other available products.
The Science Behind Pill Formulation
Pill formulation is a complex process that requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure the medication is both effective and user-friendly. At the heart of this process lies the need for bulking agents, which play a vital role in creating pills that are easy to handle, swallow, and digest.
Understanding Bulking Agents in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
Bulking agents, often referred to as fillers or diluents, are inactive substances incorporated into medication formulations to increase the overall volume of a pill. These agents are particularly important when the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is needed only in tiny doses, as they ensure the pill remains a practical size for manufacturing and patient use. By adding bulking agents, pharmaceutical companies can produce tablets that are easier to handle, package, and administer, all while maintaining consistent dosing accuracy. Microcrystalline cellulose powder is one of the most commonly used and trusted bulking agents in this process.
The Role of MCC in Pill Composition
Microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) plays a crucial multifunctional role in pill formulation. Beyond simply adding bulk to the tablet, MCC also serves as a binder, helping to hold all ingredients together, as well as a disintegrant, promoting the tablet’s breakdown once ingested. Additionally, it can function as a lubricant during the manufacturing process to reduce friction. Its excellent compressibility allows tablets to form with strong mechanical integrity, ensuring they resist breaking during handling and storage, while also reliably delivering the active ingredients when taken by the patient.
Benefits of MCC in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
The widespread use of microcrystalline cellulose in the pharmaceutical industry is not without reason. This versatile ingredient offers numerous advantages that contribute to the quality and efficacy of medications.
Improved Pill Stability and Consistency
One of the key benefits of using MCC as a bulking agent is its ability to enhance pill stability. MCC particles have excellent binding properties, which help create cohesive tablets that resist crumbling or breaking. This stability ensures that the medication remains intact throughout its shelf life and during transportation.
Enhanced Dissolution and Bioavailability
Despite its binding properties, Microcrystalline Cellulose Powder (MCC) also functions as a disintegrant. When the pill comes into contact with water or gastric fluids, MCC particles swell and facilitate the breakdown of the tablet. This property enhances the dissolution rate of the medication, potentially improving its bioavailability and effectiveness.
Compatibility with a Wide Range of Active Ingredients
MCC is chemically inert, making it compatible with a vast array of active pharmaceutical ingredients. This compatibility is crucial in pharmaceutical formulation, as it ensures that the bulking agent does not interact with the API or alter its effectiveness. The versatility of MCC allows it to be used in various types of medications, from simple pain relievers to complex formulations for chronic conditions.
Comparing MCC to Other Bulking Agents
While microcrystalline cellulose is a popular choice for bulking agents in pharmaceutical manufacturing, it's not the only option available. Understanding how MCC compares to other bulking agents can provide valuable insights into its advantages and potential limitations.


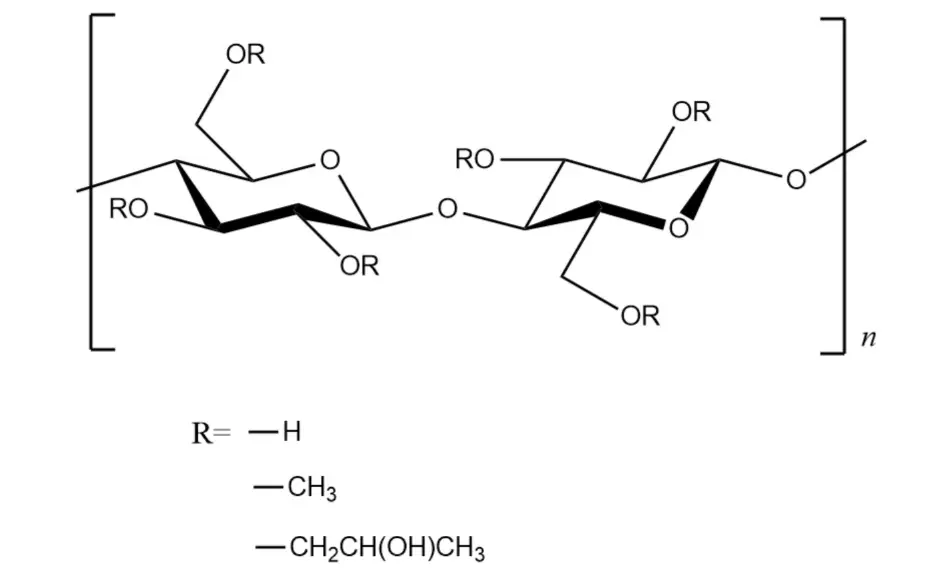
Lactose, starch, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose
MCC vs. Lactose: A Common Alternative
Lactose is another widely used bulking agent in the pharmaceutical industry. While both MCC and lactose are effective fillers, they have distinct properties that make them suitable for different applications. MCC typically offers better compressibility and faster disintegration compared to lactose. However, lactose may be preferred in certain formulations due to its sweetness, which can help mask unpleasant tastes in some medications.
Starch and Its Derivatives: How They Stack Up?
Starch and its modified forms, such as pregelatinized starch, and Microcrystalline Cellulose Powder are also used as bulking agents in pill formulation. These substances offer favorable disintegration properties but may not provide the same level of compressibility as MCC. In some cases, a combination of MCC and starch derivatives might be used to optimize both compressibility and disintegration.
Emerging Alternatives: Cellulose Derivatives and Novel Excipients
As pharmaceutical technology advances, new bulking agents are being developed and tested. These include other cellulose derivatives like hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) and novel excipients designed to address specific formulation challenges. While these alternatives show promise, microcrystalline cellulose remains a gold standard in many applications due to its well-established safety profile and versatile functionality.
Conclusion
To sum up, microcrystalline cellulose is an essential bulking ingredient in pill formation, providing a special set of qualities that enhance the efficacy and quality of pharmaceutical goods. It is a vital instrument in the pharmaceutical industry's efforts to develop better drugs because of its capacity to supply bulk, bind chemicals, promote disintegration, and preserve stability.
YTBIO provides a variety of organic solutions for pharmaceutical businesses and supplement makers who want to improve their formulations with premium, plant-based ingredients. Strict quality control procedures are used in the production of our microcrystalline cellulose powder and other plant-based excipients to guarantee that they fulfill the exacting requirements needed for pharmaceutical applications. YTBIO's knowledge of organic substances can assist you in reaching your objectives, whether you're creating new formulations or trying to enhance current ones. For additional information on how our products can enhance your pharmaceutical or nutraceutical formulations, get in touch with us at sales@sxytorganic.com.
References
1. Smith, J.A. (2022). Microcrystalline Cellulose: A Comprehensive Review of Its Applications in Pharmaceutical Formulations. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 111(5), 1243-1259.
2. Johnson, M.R., & Brown, L.E. (2021). Comparative Study of Bulking Agents in Tablet Formulation: MCC vs. Lactose. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 592, 120092.
3. Chen, X., et al. (2023). Novel Excipients in Oral Solid Dosage Forms: Challenges and Opportunities. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 180, 114-128.
4. Patel, S., & Kaushal, A.M. (2020). Functionality of Microcrystalline Cellulose and Its Impact on Tablet Properties: A Review. Journal of Excipients and Food Chemicals, 11(1), 1-12.
5. Williams, R.O., & Liu, J. (2021). Influence of Microcrystalline Cellulose Grade on Tablet Disintegration and Dissolution. AAPS PharmSciTech, 22(3), 1-10.
6. Zhang, Y., et al. (2022). Advancements in Cellulose-Based Excipients for Oral Drug Delivery Systems. Carbohydrate Polymers, 275, 118706.
_1737093401309.png)
