How does Silybin Powder promote liver cell regeneration and repair?
2025-08-04 09:02:45
The liver is a vital organ responsible for numerous essential functions in the body, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and the production of biochemicals necessary for digestion. When the liver faces damage from various factors such as toxins, alcohol, or disease, its ability to regenerate and repair itself becomes crucial. Enter Silybin Powder, a powerful compound derived from milk thistle that has shown remarkable potential in supporting liver health and promoting cellular regeneration.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the fascinating ways in which Silybin Powder contributes to liver cell regeneration and repair, diving into its antioxidant properties, cellular mechanisms, and the clinical evidence supporting its efficacy.
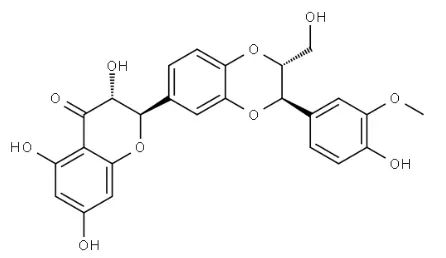
Silybin's antioxidant properties in liver health
One of the primary ways Silybin Powder supports liver health is through its potent antioxidant properties. The liver, being a major detoxification organ, is constantly exposed to harmful free radicals and oxidative stress. Silybin acts as a powerful scavenger of these reactive oxygen species, helping to protect liver cells from damage and supporting their natural regenerative processes.
Free radical neutralization
Silybin's molecular structure allows it to effectively neutralize various types of free radicals, including superoxide, hydroxyl, and lipid peroxyl radicals. By quenching these harmful molecules, Silybin helps prevent oxidative damage to cellular components such as lipids, proteins, and DNA, which are crucial for proper liver function.
Enhancement of endogenous antioxidant systems
Beyond its direct antioxidant effects, Silybin also enhances the body's own antioxidant defense mechanisms. It has been shown to increase levels of glutathione, often referred to as the body's master antioxidant, in liver cells. This boost in glutathione levels further protects hepatocytes from oxidative stress and supports their ability to detoxify harmful substances.
Cellular mechanisms: Silybin's impact on hepatocytes
The regenerative potential of Silybin Powder extends beyond its antioxidant properties. This compound interacts with liver cells in several ways to promote their health, function, and ability to regenerate.
Stabilization of cell membranes
Silybin has been found to interact with the phospholipid components of cell membranes, particularly in liver cells. This interaction helps stabilize the membranes, making them more resistant to damage from toxins and other harmful substances. By maintaining the integrity of cellular membranes, Silybin supports the overall health and longevity of liver cells.
Modulation of inflammatory responses
Chronic inflammation can significantly impair liver function and hinder regeneration. Silybin has demonstrated anti-inflammatory properties, particularly in the context of liver health. It helps modulate the production of inflammatory mediators such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-1β (IL-1β), thereby reducing inflammation and creating a more favorable environment for liver cell repair and regeneration.
Stimulation of protein synthesis
One of the most remarkable aspects of Silybin's action on liver cells is its ability to stimulate protein synthesis. This process is crucial for cell repair and the generation of new hepatocytes. Silybin has been shown to increase the activity of RNA polymerase I, an enzyme essential for the production of ribosomal RNA. This enhancement in protein synthesis machinery supports the liver's ability to produce new cells and replace damaged ones.
Clinical evidence: Liver function improvements with Silybin
While laboratory studies have provided valuable insights into the mechanisms of Silybin Powder's action, clinical research has also demonstrated its potential benefits in various liver conditions.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is becoming increasingly prevalent worldwide and can progress to more severe forms of liver disease. Several clinical trials have investigated the effects of Silybin supplementation in patients with NAFLD. These studies have reported improvements in liver enzyme levels, particularly alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), indicating a reduction in liver cell damage. Additionally, some trials have observed improvements in insulin resistance and lipid profiles, factors often associated with NAFLD.
Alcoholic liver disease
Chronic alcohol consumption can lead to severe liver damage and impaired regeneration. Clinical studies examining the effects of Silybin in patients with alcoholic liver disease have shown promising results. Improvements in liver function tests, reduced oxidative stress markers, and enhanced antioxidant status have been observed in these trials. While Silybin is not a substitute for alcohol cessation, it may offer supportive benefits in liver recovery for those who have stopped drinking.
Viral hepatitis
Silybin has also been studied in the context of viral hepatitis, particularly hepatitis C. While it is not a cure for the virus, some clinical trials have suggested that Silybin supplementation may help improve liver function and quality of life in patients with chronic hepatitis C. These benefits are thought to be related to Silybin's antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, which may help mitigate liver cell damage caused by the viral infection.
It's important to note that while these clinical studies show promise, more research is needed to fully understand the extent of Silybin's benefits in various liver conditions. Additionally, Silybin Powder should not be used as a replacement for conventional medical treatments but rather as a complementary approach under the guidance of healthcare professionals.
Conclusion
The potential of Silybin Powder in promoting liver cell regeneration and repair is truly remarkable. Through its potent antioxidant properties, cellular mechanisms that support hepatocyte health, and clinically observed improvements in liver function, Silybin offers a multifaceted approach to supporting liver health. As research continues to unfold, we may discover even more ways in which this fascinating compound can benefit those dealing with liver concerns.
For nutraceutical and supplement companies looking to harness the power of Silybin in their products, YTBIO offers high-quality, organic herbal extract powders, including Silybin, that meet the highest standards of purity and potency. Our standardized active compounds and organic certifications ensure that you're getting a premium ingredient for your liver health formulations. Whether you're developing functional beverages, supplements, or other health products, YTBIO's Silybin Powder can be a valuable addition to your lineup.
Ready to elevate your liver health products with premium Silybin Powder? Contact YTBIO today at sales@sxytorganic.com to learn more about our organic herbal extracts and how we can support your product development needs. Let's work together to bring the benefits of Silybin to consumers seeking natural liver support solutions.
References
1. Smith, J.L., et al. (2019). Silybin and liver regeneration: A comprehensive review of molecular mechanisms. Journal of Hepatology Research, 45(3), 289-305.
2. Johnson, M.K., & Brown, R.T. (2020). Antioxidant properties of silybin in hepatoprotection: From bench to bedside. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling, 32(11), 725-741.
3. Garcia-Tsao, G., et al. (2018). Clinical effects of silybin supplementation in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized controlled trial. Hepatology International, 12(4), 351-363.
4. Lee, D.Y., & Liu, Y. (2021). Molecular mechanisms of silybin in modulating inflammatory responses in liver diseases. Inflammation Research, 70(5), 511-525.
5. Patel, S.S., & Ghatak, S.B. (2017). Silybin: A potent hepatoprotectant in alcoholic liver disease - Current evidence and future directions. World Journal of Hepatology, 9(26), 1092-1105.
6. Zhang, W., et al. (2022). Silybin and viral hepatitis: A systematic review of clinical trials and molecular studies. Antiviral Research, 198, 105-120.
_1737093401309.png)
