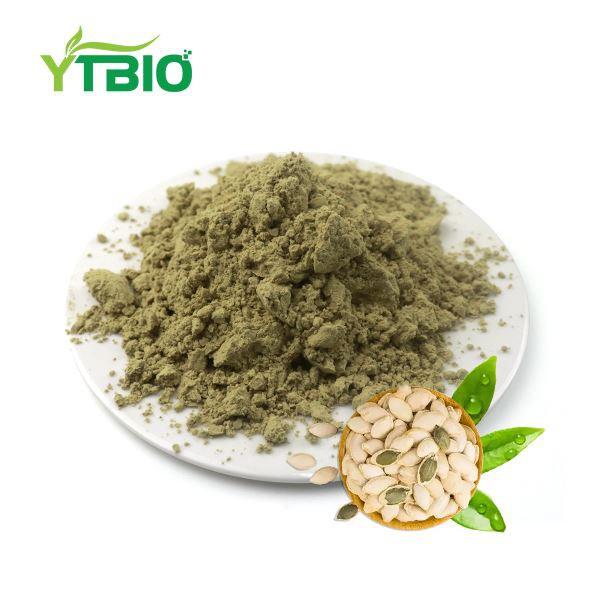
Organic Pumpkin Seed Protein
Specification: Protein>70%
Appearance:Greenish or shallow green powder
Application :Food, Health Products And Medical Fields
Shipping Speed:3-5 days
Certifications : cGMP,ISO22000,ISO9001,EU&NOP Organic Certificate,Kosher,BRC,Halal,HACCP
Sample: Available
Storage:Cool Dry Place
- Fast Delievery
- Quality Assurance
- 24/7 Customer Service
Product Introduction
Do You Know About Organic Pumpkin Seed Protein?
Organic Pumpkin seed protein is extracted from the mature seeds of Cucurbita moschata (Duch.) Poiret., a plant of the Cucurbitaceae family. Pumpkin seeds, also known as pumpkin kernels, white pumpkin seeds, and golden pumpkin seeds, are rich in nutrients, containing approximately 50% fat and 30%-40% protein. After defatting, pumpkin seed protein can reach over 60%. Its protein also has a rich amino acid profile, making it a good source of plant protein.
Organic Pumpkin Seed Protein Powder is a natural pumpkin protein certified organic by the EU and the US. It is a fine off-white to greenish-white powder with a nitrogen content generally greater than or equal to 60%, determined using the Kjeldahl method.

What are the main ingredients of Organic Pumpkin seed protein?
The main components of organic pumpkin seed protein include cucurbitine, protein, fatty oils, and various vitamins and minerals.
Cucurbitine: A naturally occurring organic compound with anthelmintic properties, paralyzing parasites such as tapeworms and schistosoma larvae.
Protein: Contains over 60% protein and a rich amino acid profile, making it a high-quality plant protein source.
Fat oils: Rich in glycerides such as linoleic acid and oleic acid.
Other ingredients: Contains vitamin A, B vitamins, dietary fiber, and minerals such as zinc, magnesium, and iron.
What are the properties of Organic Pumpkin seed protein?
Hydration Properties
Pumpkin seed protein's peptide chain backbone contains many polar groups, making it highly absorbent, water-retaining, and swellable.
Emulsifying Properties
Pumpkin seed protein is a surfactant that reduces the surface tension of both water and oil, as well as that of water and air. It easily forms stable emulsions. In baked goods, frozen foods, and soups, adding pumpkin seed protein as an emulsifier stabilizes the finished product.
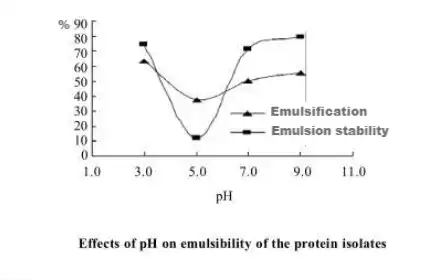
Gelling Properties
Pumpkin seed protein has high viscosity, plasticity, and elasticity. It can serve as a carrier for water, flavors, sugars, and other compounds, helping to maintain a stable surface. This is highly beneficial in food processing.
Foaming Properties
Utilizing the foaming properties and bubble stability of pumpkin seed protein can impart a loose structure and a pleasant mouthfeel to foods.
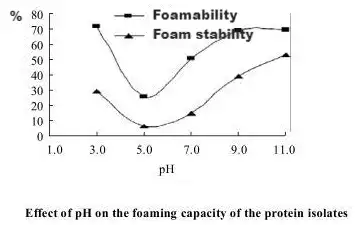
What Are The Benefits Of Organic Pumpkin Seed Protein?
Pumpkin seed protein's rich nutritional profile offers a range of health benefits.
Rich in Essential Amino Acids
Pumpkin seed protein contains all nine essential amino acids required by the human body. Arginine helps promote nitric oxide production and improve blood circulation, while glutamine supports intestinal mucosal repair and immune function. It is an excellent source of plant protein for vegetarians or those experiencing insufficient protein intake.
Cholesterol Regulators
The phytosterols (such as beta-sitosterol) in pumpkin seeds competitively inhibit cholesterol absorption, lowering low-density lipoprotein (LDL) levels and reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory
Rich in antioxidants such as vitamin E and phenolic compounds, pumpkin seed protein neutralizes free radicals and mitigates oxidative stress. Its anti-inflammatory properties may help alleviate chronic inflammatory conditions such as arthritis.
Mineral Supplementation
It contains minerals such as magnesium, zinc, and iron. Magnesium helps maintain heart and nerve function; zinc is essential for prostate health, immune regulation, and wound healing.
Cardiovascular Protection
Pumpkin seed protein is cholesterol-free and can be used as an alternative to animal protein, mitigating the risk of arteriosclerosis caused by excessive dietary cholesterol intake. It is rich in arginine, which promotes nitric oxide synthesis, thereby dilating blood vessels, lowering blood pressure, improving blood flow to the heart and brain, enhancing vascular elasticity, and preventing cardiovascular disease.
Immune Enhancement
It boosts humoral immunity by stimulating immunoglobulin synthesis; promotes T lymphocyte proliferation, strengthening cellular immunity; and regulates various hormones (such as insulin and growth hormone), indirectly improving immune function.
Reproductive Health
It improves sperm motility and quality, enhancing fertilization ability. Arginine, as a key component of sperm nucleoprotein, improves erectile function through the nitric oxide pathway.
What Are The Applications Of Pumpkin Seed Protein?
Organic Pumpkin seed protein's applications primarily include food, health supplements, and pharmaceuticals.
Food
Nutritional supplements: Pumpkin seed protein can be used as an additive to grains like flour and cornmeal to compensate for deficiencies in essential amino acids (such as lysine) and improve the nutritional value of the grains.
Baking: It can be used in baked goods like bread and pastries to increase protein content and enhance flavor.
Meat products: It can be added to meat products to improve texture and flavor while also increasing protein content.
Dairy products: It can be used in cholesterol-free products like plant-based milk and plant-based yogurt.
Beverages: Pumpkin seed kernel powder can be used to make beverages that offer a unique taste and are rich in nutrients.
Health supplements
Pumpkin seed protein can be added to health supplements for cardiovascular health, immune support, and antioxidant benefits.
Pharmaceuticals
As a pharmaceutical additive, pumpkin seed protein can be used as an adjunct to the treatment of schistosomiasis. It can also maintain normal prostate function and prevent prostate disease.
Organic Pumpkin Seed Protein: One Of The Best Plant Proteins
Plant-Based Protein Trends Positive
The global plant-based trend shows that 42% of consumers now consider protein to be the most important ingredient. The market has responded accordingly, with a steady increase in product launches labeled "high in protein" or "containing a protein source" over the past few years.
As demand for protein continues to rise, protein marketing is becoming increasingly diverse. Beyond the traditional sports nutrition sector, protein is being promoted for a variety of benefits, including boosting energy and endurance, aiding weight management, and enhancing immunity, while muscle building has become less of a priority than in previous years. This diversification is also reflected within product categories, with categories such as desserts and ice cream, dairy products, and ready-to-eat meals, which traditionally haven't emphasized protein content, seeing an increase in the number of products with protein-related claims.
While the use of all protein ingredients is growing, plant-based proteins are particularly strong, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7%, compared to a 3% CAGR for all other protein ingredients. Plant-based products with natural ingredients are likely to appeal to the 25% of consumers who are hesitant to purchase plant-based products due to concerns about over-processing. This demonstrates that the potential of plant-based proteins can be further unlocked when their formulations cater to consumer demand for natural foods.
Advantages and Limitations of Plant Protein
·Main Sources
Plant-based proteins typically come from whole grains, nuts, seeds, beans, lentils, and soy. They are widely used in sports supplements and the food industry.

·Advantages
Plant protein is rich in micronutrients: Compared to whey protein, plant protein generally contains higher levels of vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and dietary fiber. It is suitable for vegetarians, those with lactose intolerance, or those with dairy allergies.
·Limitations
Despite its advantages, plant protein still faces challenges regarding amino acid completeness, bioavailability, and potential health risks:
·Soy protein
The phytoestrogens (isoflavonoids) in soy protein may affect endocrine function, but their long-term effects are not fully established. Antinutrients (phytates) may reduce the absorption of minerals such as iron and zinc. Due to its low methionine content, it is not considered a "complete protein." Soy is also a common allergen.
·Pea protein
While it contains all nine essential amino acids (EAAs), it is low in methionine and cysteine (EAAs are only 30%) and may not meet the criteria for a complete protein.
·Brown rice protein
Brown rice protein is low in lysine and contains only 28% EAA, making it a non-complete protein. It may be contaminated with lead (especially when mixed with cocoa, which can also contain lead). Its taste is poor, with a powdery or sandy texture that leaves consumers with a less than ideal experience.
Pumpkin Seed Protein – Excellent Plant Protein
Plant-based proteins are growing in popularity, but there's still room for improvement in sourcing, taste, and texture.
Pumpkin seed protein is perhaps the best of the bunch, representing the pinnacle of plant-based protein in terms of quality and experience.
With a robust amino acid profile comparable to other options while also rivaling whey in taste and texture, pumpkin seed protein offers a unique plant-based protein powder option that can compete with beloved dairy proteins.
Nutritional Advantages: Surpassing Ordinary Plant Proteins
Organic Pumpkin seed protein’s unique value lies in its comprehensive nutritional density: It is rich in minerals, with prominent zinc, magnesium, and iron content, which improve immunity, hormone balance, and sleep. It also contains vitamins E, K, and omega-3s, supporting cardiovascular and anti-inflammatory health. It is lactose-free and soy-free, making it suitable for those with allergies.

·Good Taste: Creamy texture similar to whey
Compared to pea or brown rice protein, high-quality pumpkin seed protein powder has a smooth texture closer to whey, without noticeable graininess, addressing the common issues of vegan protein: a heavy powdery texture and a poor aftertaste.
·Challenges
Currently, pumpkin seed protein faces some risks. The cost of direct protein extraction (non-residue utilization) is higher than that of soy or pea protein. Furthermore, it must be blended with pea or brown rice protein to compensate for the lack of EAAs, and even then, it still struggles to fully match the muscle-building efficiency of whey.
·Future Goals
While pumpkin seed protein isn't perfect, its comprehensive nutritional profile, taste, and hypoallergenic properties make it a promising candidate for plant-based protein. Hopefully, in the future, products with more precise and perfect formulations will be developed, improving extraction efficiency and reducing costs, ultimately driving further market development.
Summary
Pumpkin seed protein isn't the best plant-based protein, but it's currently the closest alternative to whey. For those seeking taste, nutrition, and vegetarian-friendliness, it's a high-quality whey alternative. For those seeking muscle growth, it's recommended to combine it with other proteins to optimize amino acid intake. With technological advancements, pumpkin seed protein may become a significant driver of the plant-based protein market.
YTBIO is developing in an all-round way. We have our own factory, quality inspection and R&D team. We are committed to providing customers with the best quality Organic Pumpkin seed protein Powder and services. It is our original intention to let every consumer enjoy high-quality and healthy products. If you have any needs or questions about our products, please feel free to contact us and we will reply you as soon as possible.
_1737093401309.png)

