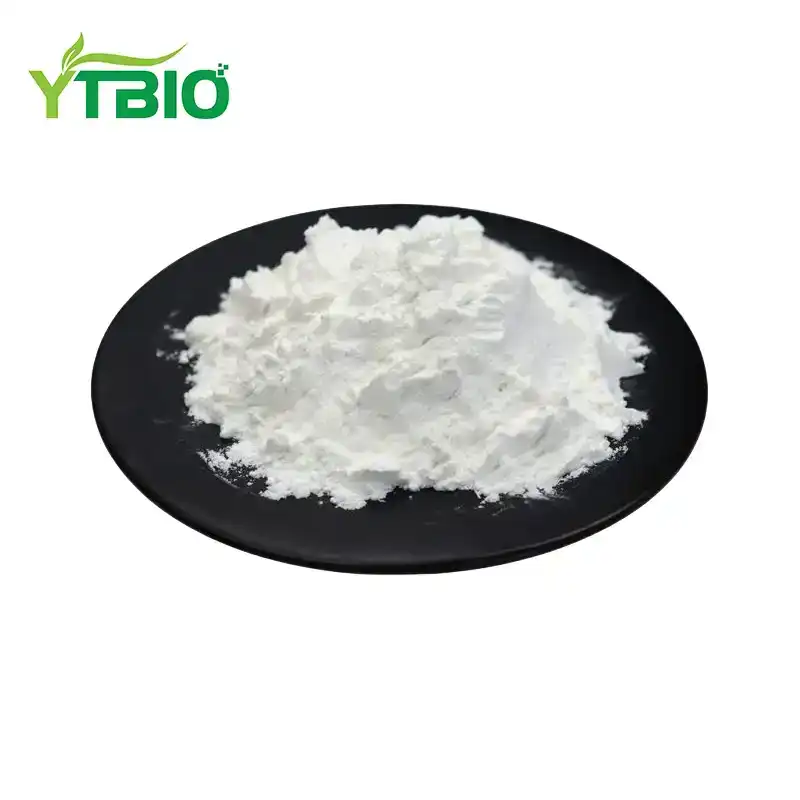
Pepsin Powder
Specification: 3000iu/g,10000iu/g
Detection Method:HPLC
Packaging: 25kg/drum
Storage: Cool, Dry, Away From Light
Shipping Speed: 3-5 days
Certification:cGMP,ISO22000,ISO9001,EU&NOP Organic Certificate,Kosher,BRC,Halal,HACCP
- Fast Delievery
- Quality Assurance
- 24/7 Customer Service
Product Introduction
What Is Pepsin Powder?
Pepsin is a digestive protease that primarily breaks down food proteins into peptides. It is produced by pepsinogen, a enzyme secreted by gastric mucosal progenitor cells in the stomach, and then stimulated by pepsin to form pepsin. Pepsin is the primary digestive enzyme in gastric juice and is synthesized by chief cells of the gastric glands from amino acids. During digestion, pepsin is released into the stomach cavity to help break down food. When digestion ceases, its synthesis restarts to replenish consumption and maintain adequate reserves. Pepsin is primarily extracted from the gastric mucosa of animals (such as pigs, cattle, and sheep). Its core function is to promote protein digestion and absorption. As an acidic protease, pepsin powder is currently used in the food industry and pharmaceuticals.
Pepsin plays a central role in protein digestion, but it is initially secreted by chief cells as an inactive precursor, pepsinogen. Pepsinogen can be likened to a zymogen with a protective sheath and has no digestive function on its own. When it comes into contact with gastric acid and a small amount of activated pepsin, it becomes activated and converted into pepsin, which has digestive activity and participates in the breakdown of food proteins. This enzyme hydrolyzes peptide bonds within protein molecules, breaking them down into simpler components for further and more complete digestion in the small intestine.
Production Method
Currently, there are two methods for producing pepsin powder: alkaline extraction and acid extraction. Acid extraction is simple, using hydrochloric acid or citric acid as a buffer solution to directly obtain mature pepsin. Alkaline extraction, on the other hand, uses an alkaline buffer solution to obtain pepsinogen, a semi-finished product that requires subsequent purification. This process is lengthy and time-consuming, and the resulting product is high in impurities and low in enzyme content. Most known pepsins are primarily extracted using the alkaline method, primarily because the final product obtained from this process is pepsinogen, which facilitates subsequent research and long-term storage.
YTBIO: Providing High-Quality pepsin powder and Services
High-quality nutritional supplements are crucial to your health journey. YTBIO specializes in providing high-quality pepsin powder.
Why choose YTBIO? We hold the following certifications:
- cGMP, ISO9001, and ISO22000 certifications ensure rigorous quality control throughout the entire process;
- BRC and HACCP system certifications ensure product safety and reliability;
- EU and NOP organic, kosher, and halal certifications meet various global standards and dietary requirements.
We specialize in the research, development, and production of natural plant extracts, cosmetic active ingredients, and health foods. We primarily produce plant extracts, health food ingredients, and a variety of end-use products, including capsules, softgels, granular capsules, gummies, tablets, and solid beverages. Our production facilities and equipment meet national standards, and our production processes strictly adhere to GMP requirements. If you have any questions, please feel free to contact us at sales@sxytorganic.com
What Does Pepsin Powder Do?
Core Digestive Functions
Activated by gastric acid, pepsin powder efficiently breaks down proteins in food, converting them into small peptides and amino acids, preparing them for absorption and utilization by the body.

Improving Nutrient Utilization
By promoting protein degradation, pepsin not only helps the body absorb protein nutrients but also creates favorable conditions for the absorption of other nutrients, thereby improving overall nutrient absorption efficiency.
Regulating the Gastric Environment
Pepsin activity helps maintain a normal acidic state in the stomach, which inhibits the growth of pathogenic microorganisms and pre-processes certain foreign proteins, reducing the potential for allergic or immune reactions.
Immune Support
Pepsin breaks down potentially allergenic and pathogenic proteins in food, reducing the burden on the immune system and helping maintain intestinal immune stability.
Improving Digestive Discomfort
For those with insufficient pepsin secretion, such as the elderly or those with chronic gastritis, appropriate exogenous pepsin powder supplementation can aid protein digestion and alleviate bloating, belching, and abdominal discomfort caused by indigestion.
Key Applications of Pepsin powder in the Food Industry
1. Promoting Protein Absorption and Nutritional Supplementation
Pepsin effectively breaks down large protein molecules in food into smaller, more easily absorbed peptides and amino acids. This property makes it a common addition to specific functional foods or dietary supplements, aiming to improve nutrient absorption for individuals with poor digestion or protein malabsorption.
2. Optimizing Food Ingredients and Processing Quality
In industrial processing, pepsin is used to treat a variety of protein-rich ingredients (such as meat and soy products). By hydrolyzing proteins in a targeted manner, it can improve the texture and mouthfeel of the final product, such as enhancing the tenderness of meat and producing hypoallergenic protein hydrolyzed products, thereby enhancing the overall quality and digestibility of the food.
3. Developing Foods for Special Uses
Pepsin can be used to modify the structure and form of proteins in food for specific needs, such as those with dysphagia and impaired digestion. For example, in the development of soft or gel-like special diets, enzymatic treatment can make proteins easier to swallow and digest, improving the physical properties of the product and meeting the nutritional and health needs of the user.
How much do you know about biological proteases?
Protease is the most important industrial enzyme preparation that can catalyze the hydrolysis of peptide bonds in proteins and polypeptides. It is widely found in animal offal, plant stems and leaves, fruits and microorganisms.
Classification
According to the way proteases hydrolyze proteins, they can be divided into the following categories:
(1) Cutting the peptide bonds inside protein molecules to generate peptides with relatively small molecular weight. Such enzymes are generally called endopeptidases;
(2) Cutting the peptide bonds at the amino or carboxyl end of protein or polypeptide molecules to release amino acids. Such enzymes are called exopeptidases. Those that act on the amino end are called aminopeptidases, and those that act on the carboxyl end are called carboxypeptidases;
(3) Hydrolyzing the lipid bonds of proteins or polypeptides;
(4) Hydrolyzing the amide bonds of proteins or polypeptides.
According to the source of enzymes, they can be divided into animal proteases(such as pepsin powder), plant proteases and microbial proteases.
Uses of proteases
Food fermentation industry
In soy sauce brewing, proteases (such as the enzyme secreted by Aspergillus oryzae) can decompose raw proteins to generate peptides and amino acids that give flavor. In beer brewing, proteases are used to supplement protein degradation and prevent turbidity. In fish sauce production, the addition of proteases can significantly shorten the natural fermentation cycle and enhance the flavor.
Leather Industry
Proteases selectively break down the non-fibrous interstitial proteins in raw hides and skins, preserving the useful collagen fibers. This allows for effective enzymatic dehairing, making the finished leather softer and less brittle.
Gelatin and Collagen Fiber Production
Compared to traditional limewater treatment, using proteases to purify collagen significantly shortens the production cycle, improves gelatin yield and quality, and produces a more uniform molecular weight and structured product.
Wool Low-Temperature Dyeing
Wool pretreated with proteases can be dyed quickly and evenly at lower temperatures, avoiding damage to wool fibers caused by high temperatures. It also results in a brighter color, a richer feel, and reduced dye residue.
Silk Degumming
Sericin in raw silk is a protein. Protease degumming can replace the traditional alkali soap method. This method uses mild conditions and effectively protects silk fibers, resulting in a brighter, softer silk finish. It also improves production efficiency and reduces energy consumption.
Comparison of common proteases
|
|
Animal Proteases |
Plant Proteases |
Microbial Proteases |
|
Main Sources |
Animal organs (pancreas, stomach), tissues |
Fruits, stems, and leaves of plants (papaya, pineapple, and figs) |
Bacteria (such as Bacillus subtilis), Fungi (such as Aspergillus oryzae) |
|
Typical Representatives |
Trypsin, pepsin powder, chymotrypsin |
Papain, bromelain, and ficin |
Subtilisin, Neutral Protease, Alkaline Protease |
|
Main Advantages |
1. High catalytic efficiency and strong specificity 2. Good biocompatibility, suitable for pharmaceutical and scientific research 3. Mild reaction conditions |
1. Naturally derived, highly safe, and widely accepted by consumers 2. Commonly used in food and cosmetics 3. Relatively simple extraction process |
1. Lowest production cost, easy to scale up industrially
2. Extremely high yield, unrestricted by seasonality or geographic location
3. Easily modified through genetic engineering (to improve stability, activity, etc.)
4. Rich and comprehensive enzyme portfolio |
|
Main Disadvantages |
1. Limited sources, influenced by the slaughtering industry, resulting in high costs 2. Limited production, difficult to mass-produce 3. High risk of carrying animal pathogens 4. Ethical and religious issues Medical fields (digestive aids, anti-inflammatory and debridement), biological research (protein sequencing, cell digestion), high-end cosmetics |
1. Unstable yields, affected by planting area, climate, and season. 2. Requires large land area and is more expensive than microbial sources. 3. Enzymatic properties (such as thermal stability) are generally inferior to those of microbial sources. |
1. Some consumers have safety concerns about "genetically modified microorganisms" (despite being very safe)
2. Complex fermentation broth composition, potentially leading to high downstream purification costs |
|
Main Applications |
Pharmaceuticals (digestive aids, anti-inflammatory and debridement), biological research (protein sequencing, cell digestion), high-end cosmetics |
Food industry (beer clarification, meat tenderization, biscuit processing), cosmetics (exfoliation, skin care products), traditional medicine |
Detergent industry (largest market, stain removal), leather industry (dehairing, softening), food fermentation (soy sauce, cheese), feed additives, wastewater treatment |
YTBIO has own factory and R&D team, dedicated to providing you with high-quality pepsin powder, and services. If you have any questions or needs, please contact us and we will respond to you as soon as possible.
FAQ
Q: What certifications do you hold?
A: We prioritize product quality and safety, and our production facilities hold several top international certifications, including:
· cGMP
· ISO9001 and ISO22000
· BRC
· HACCP
· EU and NOP organic certifications
· Kosher certification
· Halal certification
Q: Do you provide third-party test reports (COAs) for your products?
A: Of course. We provide a COA with every batch.
Q: Do you offer custom products and technical support?
A: Yes, we have a strong R&D team. In addition to standard products, we can also provide customized dosage forms and customized packaging to meet your specific needs.
Our technical team is always ready to provide comprehensive technical support, including product application and formulation advice.
_1737093401309.png)

